0x00 前言
Netflix 工程师开发的 Gadget Inspector 是一个用于挖掘 Java 反序列化漏洞利用链的工具,网上有两个同名资料 Automated Discovery of Deserialization Gadget Chains:论文 、PPT 。看懂工作流程并不难,入口类非常清晰明了,主要是逆拓扑排序、JVM 模拟(本地变量表、操作数栈)的部分比较晦涩。鉴于我四舍五入算是零基础接触 Java,所以前面先补充一些相关知识,后面再详细解析 Gadget Inspector 的代码。
加了注释的源码:jckling/gadgetinspector
0x01 预备知识
1.1 Java 字节码
看美团的 字节码增强技术探索 里面的介绍就够了,内容包括 java 的字节码、asm 框架、Javassist 框架以及 instrument 类库。
限定名(qualified names) :名称、.、标识符,例如:demo.servlet.HelloServlet,有些地方用 / 代替点号
简单名称(simple name) :单个标识符,例如:test
完全限定名(fully qualified names) :每个原始类型、命名包、顶级类和顶级接口都有一个完全限定名,有的是简单名称有的是限定名,详见 6.7. Fully Qualified Names and Canonical Names
描述符(Descriptor)
字段(Field)描述符
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 FieldDescriptor: FieldType FieldType: BaseType ObjectType ArrayType BaseType: B C D F I J S Z ObjectType: L ClassName ; ArrayType: [ ComponentType ComponentType: FieldType
说明
BaseType Character
Type
Interpretation
B
byte
signed byte
C
char
Unicode character code point in the Basic Multilingual Plane, encoded with UTF-16
D
double
double-precision floating-point value
F
float
single-precision floating-point value
I
int
integer
J
long
long integer
L
ClassName
; reference an instance of class ClassName
S
short
signed short
Z
boolean
true or false
[
reference
one array dimension
方法(Method)描述符
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 MethodDescriptor: ( ParameterDescriptor* ) ReturnDescriptor ParameterDescriptor: FieldType ReturnDescriptor: FieldType VoidDescriptor VoidDescriptor: V
1.2 JVM
Gadget Inspector 的 TaintTrackingMethodVisitor 中模拟了 JVM 的本地变量表(Local Variable Table)和操作数栈(Operand Stack),用于进行污点分析。
栈帧(Stack Frame) 是用于支持虚拟机进行方法调用和方法执行的数据结构,每个方法从调用到执行完成的过程,都对应着一个栈帧在虚拟机栈里从入栈到出栈的过程。
本地变量表(Local Variable Table) 存储了方法参数和方法内定义的局部变量,隐式传入实例对象本身 this 。
操作数栈(Operand Stack) 由操作码控制元素的出/入栈,操作数栈中的元素可以是任意 Java 数据类型。
入栈:本地变量表或对象实例的字段中的元素(常量/变量)
出栈:将栈中元素写入本地变量表或返回给方法调用者(返回栈顶)
栈中元素的长度可能为 0、1、2,这里一个单位为 32 位
1.3 ASM
访问者模式
访问者模式的核心思想是为了访问比较复杂的数据结构,不去改变数据结构,而是把对数据的操作抽象出来,在“访问”的过程中以回调形式在访问者中处理操作逻辑 。如果要新增一组操作,那么只需要增加一个新的访问者。
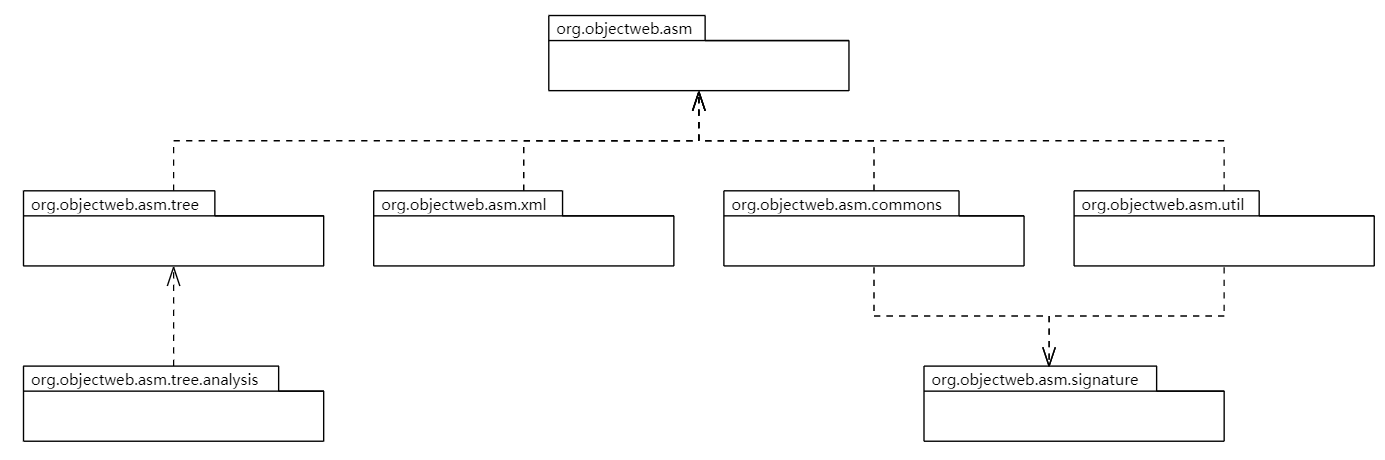
代码组织架构
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 org.objectweb.asm org.objectweb.asm.commons org.objectweb.asm.signature org.objectweb.asm.tree org.objectweb.asm.tree.analysis org.objectweb.asm.util org.objectweb.asm.xml
工作流程
ClassReader 类解析 class 文件(事件生成)
调用作为参数传递给 accept 方法的 ClassVisitor 实例上相应的 visitXxx 方法
ClassVisitor 类将所有方法调用委派给另一个 ClassVisitor 实例(事件过滤)
ClassWriter 类是 ClassVisitor 抽象类的子类(事件消费)
为了对类文件进行“观察”,需要继承和重写访问者(Visitor),然后调用 ClassReader.accept 方法执行访问,该方法将按顺序调用参数 ClassVisitor 中的方法,没有重写的则调用父类 ClassVisitor 默认的方法;观察到方法时,将按顺序调用 MethodVisitor 中的方法,没有重写的也调用默认方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public ClassReader(byte [] classFile)public void accept(ClassVisitor classVisitor, int parsingOptions)
访问者
1. ClassVisitor
方法调用顺序(访问顺序)
1 visit [ visitSource ] [ visitModule ][ visitNestHost ][ visitOuterClass ] ( visitAnnotation | visitTypeAnnotation | visitAttribute )* ( visitNestMember | [ * visitPermittedSubclass ] | visitInnerClass | visitRecordComponent | visitField | visitMethod )* visitEnd
Gadget Inspector 中涉及的方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 public ClassVisitor(int api)public void visit (int version, int access, java.lang.String name, java.lang.String signature, java.lang.String superName, java.lang.String[] interfaces) public void visitOuterClass (java.lang.String owner, java.lang.String name, java.lang.String descriptor) public void visitInnerClass (java.lang.String name, java.lang.String outerName, java.lang.String innerName, int access) public FieldVisitor visitField(int access, java.lang.String name, java.lang.String descriptor, java.lang.String signature, java.lang.Object value)public MethodVisitor visitMethod (int access, java.lang.String name, java.lang.String descriptor, java.lang.String signature, java.lang.String[] exceptions) public void visitEnd ()
2. MethodVisitor
方法调用顺序(访问顺序),visit<i>X</i>Insn 按照字节码指令顺序调用。
1 2 3 ( visitParameter )* [ visitAnnotationDefault ] ( visitAnnotation | visitAnnotableParameterCount | visitParameterAnnotation visitTypeAnnotation | visitAttribute )* [ visitCode ( visitFrame | visit<i>X</i>Insn | visitLabel | visitInsnAnnotation | visitTryCatchBlock | visitTryCatchAnnotation | visitLocalVariable | visitLocalVariableAnnotation | visitLineNumber )* visitMaxs ] visitEnd In addition, the visit<i>X</i>Insn and visitLabel methods must be called in the sequential order of the bytecode instructions of the visited code.
Gadget Inspector 中涉及的方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 public void visitCode () public void visitFrame (int type, int numLocal, java.lang.Object[] local, int numStack, java.lang.Object[] stack) public void visitInsn (int opcode) public void visitIntInsn (int opcode, int operand) public void visitVarInsn (int opcode, int var ) public void visitTypeInsn (int opcode, java.lang.String type) public void visitFieldInsn (int opcode, java.lang.String owner, java.lang.String name, java.lang.String descriptor) public void visitMethodInsn (int opcode, java.lang.String owner, java.lang.String name, java.lang.String descriptor, boolean isInterface) public void visitInvokeDynamicInsn (java.lang.String name, java.lang.String descriptor, Handle bootstrapMethodHandle, java.lang.Object... bootstrapMethodArguments) public void visitJumpInsn (int opcode, Label label) public void visitLabel (Label label) public void visitLdcInsn (java.lang.Object value) public void visitIincInsn (int var , int increment) public void visitTableSwitchInsn (int min, int max, Label dflt, Label... labels) public void visitLookupSwitchInsn (Label dflt, int [] keys, Label[] labels) public void visitMultiANewArrayInsn (java.lang.String descriptor, int numDimensions) public AnnotationVisitor visitInsnAnnotation (int typeRef, TypePath typePath, java.lang.String descriptor, boolean visible) public void visitTryCatchBlock (Label start, Label end, Label handler, java.lang.String type) public AnnotationVisitor visitTryCatchAnnotation (int typeRef, TypePath typePath, java.lang.String descriptor, boolean visible) public void visitMaxs (int maxStack, int maxLocals) public void visitEnd ()
3. FieldVisitor
方法调用顺序(访问顺序)
1 ( visitAnnotation | visitTypeAnnotation | visitAttribute )* visitEnd
其他
JSRInlinerAdapter 用于简化代码分析,删除 JSR 指令并内联引用的子例程(没懂)
A MethodVisitor that removes JSR instructions and inlines the referenced subroutines
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public JSRInlinerAdapter(MethodVisitor methodVisitor, int access, java.lang.String name, java.lang.String descriptor, java.lang.String signature, java.lang.String[] exceptions)
0x02 项目结构
项目中包含三种检测实现,在以下三个目录下:javaserial 针对 Java 原生序列化,jackson 针对 Jackson(JSON 库),xstream 针对 XStream(XML 库),同时在 config 目录下实现了各自的配置接口。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 . ├── config │ ├── ConfigRepository.java │ ├── GIConfig.java │ ├── JacksonDeserializationConfig.java │ ├── JavaDeserializationConfig.java │ └── XstreamDeserializationConfig.java ├── data │ ├── ClassReference.java │ ├── DataFactory.java │ ├── DataLoader.java │ ├── GraphCall.java │ ├── InheritanceDeriver.java │ ├── InheritanceMap.java │ ├── MethodReference.java │ └── Source.java ├── jackson │ ├── JacksonImplementationFinder.java │ ├── JacksonSerializableDecider.java │ └── JacksonSourceDiscovery.java ├── javaserial │ ├── SimpleImplementationFinder.java │ ├── SimpleSerializableDecider.java │ └── SimpleSourceDiscovery.java ├── xstream │ ├── CustomXstreamSerializableDecider.java │ └── XstreamSerializableDecider.java ├── CallGraphDiscovery.java ├── ClassResourceEnumerator.java ├── GadgetChainDiscovery.java ├── GadgetInspector.java ├── ImplementationFinder.java ├── MethodDiscovery.java ├── PassthroughDiscovery.java ├── SerializableDecider.java ├── SourceDiscovery.java ├── TaintTrackingMethodVisitor.java └── Util.java
gadgetinspector/data
主要是数据格式的定义。
1. DataLoader
定义了数据的读写方式,根据数据工厂方法(DataFactory)进行读写,loadData 返回的是动态数组,源码中多处调用进行数据遍历。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 public static <T> List<T> loadData (Path filePath, DataFactory<T> factory) throws IOException { final List<String> lines = Files.readLines(filePath.toFile(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8); final List<T> values = new ArrayList <T>(lines.size()); for (String line : lines) { values.add(factory.parse(line.split("\t" , -1 ))); } return values; } public static <T> void saveData (Path filePath, DataFactory<T> factory, Collection<T> values) throws IOException { try (BufferedWriter writer = Files.newWriter(filePath.toFile(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8)) { for (T value : values) { final String[] fields = factory.serialize(value); if (fields == null ) { continue ; } StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); for (String field : fields) { if (field == null ) { sb.append("\t" ); } else { sb.append("\t" ).append(field); } } writer.write(sb.substring(1 )); writer.write("\n" ); } } }
然后利用上面的方法实现读取类信息(classes.dat)和方法信息(methods.dat),返回存储键值的 Map,源码中多次调用用于搜索。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public static Map<ClassReference.Handle, ClassReference> loadClasses() { try { Map<ClassReference.Handle, ClassReference> classMap = new HashMap <>(); for (ClassReference classReference : loadData(Paths.get("classes.dat" ), new ClassReference .Factory())) { classMap.put(classReference.getHandle(), classReference); } return classMap; } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } public static Map<MethodReference.Handle, MethodReference> loadMethods() { try { Map<MethodReference.Handle, MethodReference> methodMap = new HashMap <>(); for (MethodReference methodReference : loadData(Paths.get("methods.dat" ), new MethodReference .Factory())) { methodMap.put(methodReference.getHandle(), methodReference); } return methodMap; } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } }
2. DataFactory
数据工厂接口,定义数据的存储格式。
1 2 3 4 public interface DataFactory <T> { T parse (String[] fields) ; String[] serialize(T obj); }
3. ClassReference
定义类信息 的描述方式,这些信息具体都使用 asm 访问者记录。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 public class ClassReference { private final String name; private final String superClass; private final String[] interfaces; private final boolean isInterface; private final Member[] members; public static class Member { private final String name; private final int modifiers; private final ClassReference.Handle type; public Member (String name, int modifiers, Handle type) { this .name = name; this .modifiers = modifiers; this .type = type; } public String getName () { return name; } public int getModifiers () { return modifiers; } public Handle getType () { return type; } } public ClassReference (String name, String superClass, String[] interfaces, boolean isInterface, Member[] members) { this .name = name; this .superClass = superClass; this .interfaces = interfaces; this .isInterface = isInterface; this .members = members; } public String getName () { return name; } public String getSuperClass () { return superClass; } public String[] getInterfaces() { return interfaces; } public boolean isInterface () { return isInterface; } public Member[] getMembers() { return members; } public Handle getHandle () { return new Handle (name); } public static class Handle { private final String name; public Handle (String name) { this .name = name; } public String getName () { return name; } @Override public boolean equals (Object o) { if (this == o) return true ; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false ; Handle handle = (Handle) o; return name != null ? name.equals(handle.name) : handle.name == null ; } @Override public int hashCode () { return name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0 ; } } ... }
定义类信息 的读写格式:类名 父类名 接口A,接口B,接口C 是否为接口 字段1!字段1访问标志!字段1类型!字段2!字段2访问标志!字段2类型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 public static class Factory implements DataFactory <ClassReference> { @Override public ClassReference parse (String[] fields) { String[] interfaces; if (fields[2 ].equals("" )) { interfaces = new String [0 ]; } else { interfaces = fields[2 ].split("," ); } String[] memberEntries = fields[4 ].split("!" ); Member[] members = new Member [memberEntries.length / 3 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < members.length; i++) { members[i] = new Member (memberEntries[3 * i], Integer.parseInt(memberEntries[3 * i + 1 ]), new ClassReference .Handle(memberEntries[3 * i + 2 ])); } return new ClassReference ( fields[0 ], fields[1 ].equals("" ) ? null : fields[1 ], interfaces, Boolean.parseBoolean(fields[3 ]), members); } @Override public String[] serialize(ClassReference obj) { String interfaces; if (obj.interfaces.length > 0 ) { StringBuilder interfacesSb = new StringBuilder (); for (String iface : obj.interfaces) { interfacesSb.append("," ).append(iface); } interfaces = interfacesSb.substring(1 ); } else { interfaces = "" ; } StringBuilder members = new StringBuilder (); for (Member member : obj.members) { members.append("!" ).append(member.getName()) .append("!" ).append(Integer.toString(member.getModifiers())) .append("!" ).append(member.getType().getName()); } return new String []{ obj.name, obj.superClass, interfaces, Boolean.toString(obj.isInterface), members.length() == 0 ? null : members.substring(1 ) }; } }
4. MethodReference
定义方法信息 的描述方式,同样使用 asm 访问者记录。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 public class MethodReference { private final ClassReference.Handle classReference; private final String name; private final String desc; private final boolean isStatic; public MethodReference (ClassReference.Handle classReference, String name, String desc, boolean isStatic) { this .classReference = classReference; this .name = name; this .desc = desc; this .isStatic = isStatic; } public ClassReference.Handle getClassReference () { return classReference; } public String getName () { return name; } public String getDesc () { return desc; } public boolean isStatic () { return isStatic; } public Handle getHandle () { return new Handle (classReference, name, desc); } public static class Handle { private final ClassReference.Handle classReference; private final String name; private final String desc; public Handle (ClassReference.Handle classReference, String name, String desc) { this .classReference = classReference; this .name = name; this .desc = desc; } public ClassReference.Handle getClassReference () { return classReference; } public String getName () { return name; } public String getDesc () { return desc; } @Override public boolean equals (Object o) { if (this == o) return true ; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false ; Handle handle = (Handle) o; if (classReference != null ? !classReference.equals(handle.classReference) : handle.classReference != null ) return false ; if (name != null ? !name.equals(handle.name) : handle.name != null ) return false ; return desc != null ? desc.equals(handle.desc) : handle.desc == null ; } @Override public int hashCode () { int result = classReference != null ? classReference.hashCode() : 0 ; result = 31 * result + (name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0 ); result = 31 * result + (desc != null ? desc.hashCode() : 0 ); return result; } } ... }
定义方法信息 的读写格式:类名 方法名 方法描述符 是否为静态方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public static class Factory implements DataFactory <MethodReference> { @Override public MethodReference parse (String[] fields) { return new MethodReference ( new ClassReference .Handle(fields[0 ]), fields[1 ], fields[2 ], Boolean.parseBoolean(fields[3 ])); } @Override public String[] serialize(MethodReference obj) { return new String [] { obj.classReference.getName(), obj.name, obj.desc, Boolean.toString(obj.isStatic), }; } }
5. inheritanceMap
定义继承信息 的描述方式,包括 子类->父类集合、父类->子类集合 两个 Map 类型变量,根据类信息得出,具体实现在 InheritanceMap 类中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 public class InheritanceMap { private final Map<ClassReference.Handle, Set<ClassReference.Handle>> inheritanceMap; private final Map<ClassReference.Handle, Set<ClassReference.Handle>> subClassMap; public InheritanceMap (Map<ClassReference.Handle, Set<ClassReference.Handle>> inheritanceMap) { this .inheritanceMap = inheritanceMap; subClassMap = new HashMap <>(); for (Map.Entry<ClassReference.Handle, Set<ClassReference.Handle>> entry : inheritanceMap.entrySet()) { ClassReference.Handle child = entry.getKey(); for (ClassReference.Handle parent : entry.getValue()) { subClassMap.computeIfAbsent(parent, k -> new HashSet <>()).add(child); } } } public Set<Map.Entry<ClassReference.Handle, Set<ClassReference.Handle>>> entrySet() { return inheritanceMap.entrySet(); } public Set<ClassReference.Handle> getSuperClasses(ClassReference.Handle clazz) { Set<ClassReference.Handle> parents = inheritanceMap.get(clazz); if (parents == null ) { return null ; } return Collections.unmodifiableSet(parents); } public boolean isSubclassOf (ClassReference.Handle clazz, ClassReference.Handle superClass) { Set<ClassReference.Handle> parents = inheritanceMap.get(clazz); if (parents == null ) { return false ; } return parents.contains(superClass); } public Set<ClassReference.Handle> getSubClasses(ClassReference.Handle clazz) { Set<ClassReference.Handle> subClasses = subClassMap.get(clazz); if (subClasses == null ) { return null ; } return Collections.unmodifiableSet(subClasses); } public void save () throws IOException { DataLoader.saveData(Paths.get("inheritanceMap.dat" ), new InheritanceMapFactory (), inheritanceMap.entrySet()); } public static InheritanceMap load () throws IOException { Map<ClassReference.Handle, Set<ClassReference.Handle>> inheritanceMap = new HashMap <>(); for (Map.Entry<ClassReference.Handle, Set<ClassReference.Handle>> entry : DataLoader.loadData( Paths.get("inheritanceMap.dat" ), new InheritanceMapFactory ())) { inheritanceMap.put(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()); } return new InheritanceMap (inheritanceMap); } ... }
定义继承信息 的读写格式(仅针对 子类->父类集合):类名 父类/超类/接口类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 private static class InheritanceMapFactory implements DataFactory <Map.Entry<ClassReference.Handle, Set<ClassReference.Handle>>> { @Override public Map.Entry<ClassReference.Handle, Set<ClassReference.Handle>> parse(String[] fields) { ClassReference.Handle clazz = new ClassReference .Handle(fields[0 ]); Set<ClassReference.Handle> superClasses = new HashSet <>(); for (int i = 1 ; i < fields.length; i++) { superClasses.add(new ClassReference .Handle(fields[i])); } return new AbstractMap .SimpleEntry<>(clazz, superClasses); } @Override public String[] serialize(Map.Entry<ClassReference.Handle, Set<ClassReference.Handle>> obj) { final String[] fields = new String [obj.getValue().size()+1 ]; fields[0 ] = obj.getKey().getName(); int i = 1 ; for (ClassReference.Handle handle : obj.getValue()) { fields[i++] = handle.getName(); } return fields; } }
6. InheritanceDeriver
实现继承信息 和重写方法信息 的收集,存储重写信息时以缩进表示重写方法,具体存储格式在 GadgetChainDiscovery 中给出。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 public class InheritanceDeriver { private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(InheritanceDeriver.class); public static InheritanceMap derive (Map<ClassReference.Handle, ClassReference> classMap) { LOGGER.debug("Calculating inheritance for " + (classMap.size()) + " classes..." ); Map<ClassReference.Handle, Set<ClassReference.Handle>> implicitInheritance = new HashMap <>(); for (ClassReference classReference : classMap.values()) { if (implicitInheritance.containsKey(classReference.getHandle())) { throw new IllegalStateException ("Already derived implicit classes for " + classReference.getName()); } Set<ClassReference.Handle> allParents = new HashSet <>(); getAllParents(classReference, classMap, allParents); implicitInheritance.put(classReference.getHandle(), allParents); } return new InheritanceMap (implicitInheritance); } private static void getAllParents (ClassReference classReference, Map<ClassReference.Handle, ClassReference> classMap, Set<ClassReference.Handle> allParents) { Set<ClassReference.Handle> parents = new HashSet <>(); if (classReference.getSuperClass() != null ) { parents.add(new ClassReference .Handle(classReference.getSuperClass())); } for (String iface : classReference.getInterfaces()) { parents.add(new ClassReference .Handle(iface)); } for (ClassReference.Handle immediateParent : parents) { ClassReference parentClassReference = classMap.get(immediateParent); if (parentClassReference == null ) { LOGGER.debug("No class id for " + immediateParent.getName()); continue ; } allParents.add(parentClassReference.getHandle()); getAllParents(parentClassReference, classMap, allParents); } } public static Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<MethodReference.Handle>> getAllMethodImplementations( InheritanceMap inheritanceMap, Map<MethodReference.Handle, MethodReference> methodMap) { Map<ClassReference.Handle, Set<MethodReference.Handle>> methodsByClass = new HashMap <>(); for (MethodReference.Handle method : methodMap.keySet()) { ClassReference.Handle classReference = method.getClassReference(); if (!methodsByClass.containsKey(classReference)) { Set<MethodReference.Handle> methods = new HashSet <>(); methods.add(method); methodsByClass.put(classReference, methods); } else { methodsByClass.get(classReference).add(method); } } Map<ClassReference.Handle, Set<ClassReference.Handle>> subClassMap = new HashMap <>(); for (Map.Entry<ClassReference.Handle, Set<ClassReference.Handle>> entry : inheritanceMap.entrySet()) { for (ClassReference.Handle parent : entry.getValue()) { if (!subClassMap.containsKey(parent)) { Set<ClassReference.Handle> subClasses = new HashSet <>(); subClasses.add(entry.getKey()); subClassMap.put(parent, subClasses); } else { subClassMap.get(parent).add(entry.getKey()); } } } Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<MethodReference.Handle>> methodImplMap = new HashMap <>(); for (MethodReference method : methodMap.values()) { if (method.isStatic()) { continue ; } Set<MethodReference.Handle> overridingMethods = new HashSet <>(); Set<ClassReference.Handle> subClasses = subClassMap.get(method.getClassReference()); if (subClasses != null ) { for (ClassReference.Handle subClass : subClasses) { Set<MethodReference.Handle> subClassMethods = methodsByClass.get(subClass); if (subClassMethods != null ) { for (MethodReference.Handle subClassMethod : subClassMethods) { if (subClassMethod.getName().equals(method.getName()) && subClassMethod.getDesc().equals(method.getDesc())) { overridingMethods.add(subClassMethod); } } } } } if (overridingMethods.size() > 0 ) { methodImplMap.put(method.getHandle(), overridingMethods); } } return methodImplMap; } }
7. GraphCall
定义污点在调用关系 中的传递信息,指的是被调用方法的参数受调用者方法的参数影响,使用 asm 访问者记录,涉及模拟 JVM 的一些操作,具体实现在 CallGraphDiscovery 类中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 public class GraphCall { private final MethodReference.Handle callerMethod; private final MethodReference.Handle targetMethod; private final int callerArgIndex; private final String callerArgPath; private final int targetArgIndex; public GraphCall (MethodReference.Handle callerMethod, MethodReference.Handle targetMethod, int callerArgIndex, String callerArgPath, int targetArgIndex) { this .callerMethod = callerMethod; this .targetMethod = targetMethod; this .callerArgIndex = callerArgIndex; this .callerArgPath = callerArgPath; this .targetArgIndex = targetArgIndex; } public MethodReference.Handle getCallerMethod () { return callerMethod; } public MethodReference.Handle getTargetMethod () { return targetMethod; } public int getCallerArgIndex () { return callerArgIndex; } public String getCallerArgPath () { return callerArgPath; } public int getTargetArgIndex () { return targetArgIndex; } @Override public boolean equals (Object o) { if (this == o) return true ; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false ; GraphCall graphCall = (GraphCall) o; if (callerArgIndex != graphCall.callerArgIndex) return false ; if (targetArgIndex != graphCall.targetArgIndex) return false ; if (callerMethod != null ? !callerMethod.equals(graphCall.callerMethod) : graphCall.callerMethod != null ) return false ; if (targetMethod != null ? !targetMethod.equals(graphCall.targetMethod) : graphCall.targetMethod != null ) return false ; return callerArgPath != null ? callerArgPath.equals(graphCall.callerArgPath) : graphCall.callerArgPath == null ; } @Override public int hashCode () { int result = callerMethod != null ? callerMethod.hashCode() : 0 ; result = 31 * result + (targetMethod != null ? targetMethod.hashCode() : 0 ); result = 31 * result + callerArgIndex; result = 31 * result + (callerArgPath != null ? callerArgPath.hashCode() : 0 ); result = 31 * result + targetArgIndex; return result; } ... }
定义读写格式:父类,父方法,父方法描述符,子类,被调方法,被调方法描述,父方法参数索引,父方法参数名,被调方法参数索引
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public static class Factory implements DataFactory <GraphCall> { @Override public GraphCall parse (String[] fields) { return new GraphCall ( new MethodReference .Handle(new ClassReference .Handle(fields[0 ]), fields[1 ], fields[2 ]), new MethodReference .Handle(new ClassReference .Handle(fields[3 ]), fields[4 ], fields[5 ]), Integer.parseInt(fields[6 ]), fields[7 ], Integer.parseInt(fields[8 ])); } @Override public String[] serialize(GraphCall obj) { return new String []{ obj.callerMethod.getClassReference().getName(), obj.callerMethod.getName(), obj.callerMethod.getDesc(), obj.targetMethod.getClassReference().getName(), obj.targetMethod.getName(), obj.targetMethod.getDesc(), Integer.toString(obj.callerArgIndex), obj.callerArgPath, Integer.toString(obj.targetArgIndex), }; } }
8. Source
定义污点源信息 的描述方式,由实现了抽象类 SourceDiscovery 的类搜索和记录。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class Source { private final MethodReference.Handle sourceMethod; private final int taintedArgIndex; public Source (MethodReference.Handle sourceMethod, int taintedArgIndex) { this .sourceMethod = sourceMethod; this .taintedArgIndex = taintedArgIndex; } public MethodReference.Handle getSourceMethod () { return sourceMethod; } public int getTaintedArgIndex () { return taintedArgIndex; } ... }
定义污点源信息 的读写格式:类名 方法名 方法描述符 参数索引
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public static class Factory implements DataFactory <Source> { @Override public Source parse (String[] fields) { return new Source ( new MethodReference .Handle(new ClassReference .Handle(fields[0 ]), fields[1 ], fields[2 ]), Integer.parseInt(fields[3 ]) ); } @Override public String[] serialize(Source obj) { return new String []{ obj.sourceMethod.getClassReference().getName(), obj.sourceMethod.getName(), obj.sourceMethod.getDesc(), Integer.toString(obj.taintedArgIndex), }; } }
gadgetinspector
实现检测需要实现的抽象类和接口,其他类的解析放到 0x03 工作流程 一节。
1. SerializableDecider
序列化决策者接口,判断类是否可序列化。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public interface SerializableDecider extends Function <ClassReference.Handle, Boolean> { }
2. ImplementationFinder
接口,用于查找可序列化的重写方法,即判断方法所属类是否可序列化。
1 2 3 public interface ImplementationFinder { Set<MethodReference.Handle> getImplementations(MethodReference.Handle target); }
3. SourceDiscovery
抽象类,实现了污点源信息的存储方法,子类需要实现污点源的具体查找方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 public abstract class SourceDiscovery { private final List<Source> discoveredSources = new ArrayList <>(); protected final void addDiscoveredSource (Source source) { discoveredSources.add(source); } public void discover () throws IOException { Map<ClassReference.Handle, ClassReference> classMap = DataLoader.loadClasses(); Map<MethodReference.Handle, MethodReference> methodMap = DataLoader.loadMethods(); InheritanceMap inheritanceMap = InheritanceMap.load(); discover(classMap, methodMap, inheritanceMap); } public abstract void discover (Map<ClassReference.Handle, ClassReference> classMap, Map<MethodReference.Handle, MethodReference> methodMap, InheritanceMap inheritanceMap) ; public void save () throws IOException { DataLoader.saveData(Paths.get("sources.dat" ), new Source .Factory(), discoveredSources); } }
gadgetinspector/config
定义配置。
1. GIConfig
配置接口,所有检测实现都必须实现该接口。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public interface GIConfig { String getName () ; SerializableDecider getSerializableDecider (Map<MethodReference.Handle, MethodReference> methodMap, InheritanceMap inheritanceMap) ; ImplementationFinder getImplementationFinder (Map<MethodReference.Handle, MethodReference> methodMap, Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<MethodReference.Handle>> methodImplMap, InheritanceMap inheritanceMap) ; SourceDiscovery getSourceDiscovery () ; }
2. ConfigRepository
定义配置列表,用于返回配置。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public class ConfigRepository { private static final List<GIConfig> ALL_CONFIGS = Collections.unmodifiableList(Arrays.asList( new JavaDeserializationConfig (), new JacksonDeserializationConfig (), new XstreamDeserializationConfig ())); public static GIConfig getConfig (String name) { for (GIConfig config : ALL_CONFIGS) { if (config.getName().equals(name)) { return config; } } return null ; } }
3. GIConfig 接口实现
JavaDeserializationConfig
配置名称:jserial
序列化决策者:gadgetinspector/javaserial/SimpleSerializableDecider
查找可序列化的重写方法:gadgetinspector/javaserial/SimpleImplementationFinder
查找污点源:gadgetinspector/javaserial/SimpleSourceDiscovery
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class JavaDeserializationConfig implements GIConfig { @Override public String getName () { return "jserial" ; } @Override public SerializableDecider getSerializableDecider (Map<MethodReference.Handle, MethodReference> methodMap, InheritanceMap inheritanceMap) { return new SimpleSerializableDecider (inheritanceMap); } @Override public ImplementationFinder getImplementationFinder (Map<MethodReference.Handle, MethodReference> methodMap, Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<MethodReference.Handle>> methodImplMap, InheritanceMap inheritanceMap) { return new SimpleImplementationFinder (getSerializableDecider(methodMap, inheritanceMap), methodImplMap); } @Override public SourceDiscovery getSourceDiscovery () { return new SimpleSourceDiscovery (); } }
JacksonDeserializationConfig
配置名称:jackson
序列化决策者:gadgetinspector/jackson/JacksonSerializableDecider
查找可序列化的重写方法:gadgetinspector/jackson/JacksonImplementationFinder
查找污点源:gadgetinspector/jackson/JacksonSourceDiscovery
XstreamDeserializationConfig
配置名称:xstream
序列化决策者:gadgetinspector/xstream/XstreamSerializableDecider、gadgetinspector/xstream/CustomXstreamSerializableDecider
查找可序列化的重写方法:gadgetinspector/javaserial/SimpleImplementationFinder
查找污点源:gadgetinspector/javaserial/SimpleSourceDiscovery
gadgetinspector/javaserial
针对 Java 原生序列化的反序列化利用链检测实现。
1. SimpleSerializableDecider
实现 SerializableDecider 接口,判断类是否可序列化。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 public class SimpleSerializableDecider implements SerializableDecider { private final Map<ClassReference.Handle, Boolean> cache = new HashMap <>(); private final InheritanceMap inheritanceMap; public SimpleSerializableDecider (InheritanceMap inheritanceMap) { this .inheritanceMap = inheritanceMap; } @Override public Boolean apply (ClassReference.Handle handle) { Boolean cached = cache.get(handle); if (cached != null ) { return cached; } Boolean result = applyNoCache(handle); cache.put(handle, result); return result; } private Boolean applyNoCache (ClassReference.Handle handle) { if (isBlacklistedClass(handle)) { return false ; } if (inheritanceMap.isSubclassOf(handle, new ClassReference .Handle("java/io/Serializable" ))) { return true ; } return false ; } private static boolean isBlacklistedClass (ClassReference.Handle clazz) { if (clazz.getName().startsWith("com/google/common/collect/" )) { return true ; } if (clazz.getName().equals("clojure/core/proxy$clojure/lang/APersistentMap$ff19274a" ) || clazz.getName().equals("clojure/inspector/proxy$javax/swing/table/AbstractTableModel$ff19274a" )) { return true ; } return false ; } }
2. SimpleImplementationFinder
实现 ImplementationFinder 接口,返回目标方法的可序列化重写方法(包括目标方法本身)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public class SimpleImplementationFinder implements ImplementationFinder { private final SerializableDecider serializableDecider; private final Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<MethodReference.Handle>> methodImplMap; public SimpleImplementationFinder (SerializableDecider serializableDecider, Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<MethodReference.Handle>> methodImplMap) { this .serializableDecider = serializableDecider; this .methodImplMap = methodImplMap; } @Override public Set<MethodReference.Handle> getImplementations(MethodReference.Handle target) { Set<MethodReference.Handle> allImpls = new HashSet <>(); allImpls.add(target); Set<MethodReference.Handle> subClassImpls = methodImplMap.get(target); if (subClassImpls != null ) { for (MethodReference.Handle subClassImpl : subClassImpls) { if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(serializableDecider.apply(subClassImpl.getClassReference()))) { allImpls.add(subClassImpl); } } } return allImpls; } }
3. SimpleSourceDiscovery
继承 SourceDiscovery 抽象类,实现具体的污点源查找方法 discover。遍历类信息和方法信息,根据定义的 5 条规则搜索污点源:
方法所属类可以序列化,且方法为无参数 void 类型的 finalize 方法
方法所属类可以序列化,且方法为接受 ObjectInputStream 类型参数的 void 类型的 readObject 方法
类可以序列化,且为 InvocationHandler 的子类
方法所属类可以序列化,且方法为无参数 int 类型的 hashCode 方法或接受 Object 类型参数的 boolean 类型的 equals 方法
方法所属类可以序列化,且该类为 groovy Closure 的子类、方法为 call 或 doCall
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 public class SimpleSourceDiscovery extends SourceDiscovery { @Override public void discover (Map<ClassReference.Handle, ClassReference> classMap, Map<MethodReference.Handle, MethodReference> methodMap, InheritanceMap inheritanceMap) { final SerializableDecider serializableDecider = new SimpleSerializableDecider (inheritanceMap); for (MethodReference.Handle method : methodMap.keySet()) { if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(serializableDecider.apply(method.getClassReference()))) { if (method.getName().equals("finalize" ) && method.getDesc().equals("()V" )) { addDiscoveredSource(new Source (method, 0 )); } } } for (MethodReference.Handle method : methodMap.keySet()) { if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(serializableDecider.apply(method.getClassReference()))) { if (method.getName().equals("readObject" ) && method.getDesc().equals("(Ljava/io/ObjectInputStream;)V" )) { addDiscoveredSource(new Source (method, 1 )); } } } for (ClassReference.Handle clazz : classMap.keySet()) { if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(serializableDecider.apply(clazz)) && inheritanceMap.isSubclassOf(clazz, new ClassReference .Handle("java/lang/reflect/InvocationHandler" ))) { MethodReference.Handle method = new MethodReference .Handle( clazz, "invoke" , "(Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;[Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;" ); addDiscoveredSource(new Source (method, 0 )); } } for (MethodReference.Handle method : methodMap.keySet()) { if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(serializableDecider.apply(method.getClassReference()))) { if (method.getName().equals("hashCode" ) && method.getDesc().equals("()I" )) { addDiscoveredSource(new Source (method, 0 )); } if (method.getName().equals("equals" ) && method.getDesc().equals("(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z" )) { addDiscoveredSource(new Source (method, 0 )); addDiscoveredSource(new Source (method, 1 )); } } } for (MethodReference.Handle method : methodMap.keySet()) { if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(serializableDecider.apply(method.getClassReference())) && inheritanceMap.isSubclassOf(method.getClassReference(), new ClassReference .Handle("groovy/lang/Closure" )) && (method.getName().equals("call" ) || method.getName().equals("doCall" ))) { addDiscoveredSource(new Source (method, 0 )); Type[] methodArgs = Type.getArgumentTypes(method.getDesc()); for (int i = 0 ; i < methodArgs.length; i++) { addDiscoveredSource(new Source (method, i + 1 )); } } } } public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { SourceDiscovery sourceDiscovery = new SimpleSourceDiscovery (); sourceDiscovery.discover(); sourceDiscovery.save(); } }
0x03 工作流程
准备工作
配置 log4j 向控制台输出日志
配置 config 为默认值 jserial(Java 反序列化)
接受参数:--resume 保留 .dat 文件、--config 指定分析类型
根据参数读取 war/jar 包路径,返回 URLClassLoader
初始化类枚举加载器 ClassResourceEnumerator
MethodDiscovery:类信息、方法信息、继承信息
classes.dat:类名、父类名、类接口名、是否为接口、类的所有字段(成员)
methods.dat:类名、方法名、描述符、是否为静态方法
inheritanceMap.dat:类名、父类/超类/接口类(直接/间接父类)
PassthroughDiscovery:数据流信息,即方法参数是否能够影响其返回值
如果存在方法将参数传递给被调方法时,需要先判断被调方法返回值与被调方法参数的关系。
passthrough.dat:类名、方法名、方法描述符、污点参数索引
CallGraphDiscovery:方法调用关系信息
callgraph.dat:方法所属类名,方法名,方法描述符,被调方法所属类名,被调方法名,被调方法描述,方法参数索引,方法参数对象的字段名称,被调方法参数索引
SourceDiscovery:查找污点源
sources.dat:类名,方法名,描述符,参数索引
GadgetChainDiscovery:重写信息、利用链信息
methodimpl.dat:类名,方法名,描述符
gadget-chains.txt:类名.方法名描述符 (参数索引)
1. Util
根据 java 包路径列表返回 URLClassLoader,后续用于读取相应的 java 包(war、jar)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 public class Util { private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Util.class); public static ClassLoader getWarClassLoader (Path warPath) throws IOException { final Path tmpDir = Files.createTempDirectory("exploded-war" ); Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread (() -> { try { deleteDirectory(tmpDir); } catch (IOException e) { LOGGER.error("Error cleaning up temp directory " + tmpDir.toString(), e); } })); try (JarInputStream jarInputStream = new JarInputStream (Files.newInputStream(warPath))) { JarEntry jarEntry; while ((jarEntry = jarInputStream.getNextJarEntry()) != null ) { Path fullPath = tmpDir.resolve(jarEntry.getName()); if (!jarEntry.isDirectory()) { Path dirName = fullPath.getParent(); if (dirName == null ) { throw new IllegalStateException ("Parent of item is outside temp directory." ); } if (!Files.exists(dirName)) { Files.createDirectories(dirName); } try (OutputStream outputStream = Files.newOutputStream(fullPath)) { copy(jarInputStream, outputStream); } } } } final List<URL> classPathUrls = new ArrayList <>(); classPathUrls.add(tmpDir.resolve("WEB-INF/classes" ).toUri().toURL()); Files.list(tmpDir.resolve("WEB-INF/lib" )).forEach(p -> { try { classPathUrls.add(p.toUri().toURL()); } catch (MalformedURLException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } }); URLClassLoader classLoader = new URLClassLoader (classPathUrls.toArray(new URL [classPathUrls.size()])); return classLoader; } public static ClassLoader getJarClassLoader (Path... jarPaths) throws IOException { final List<URL> classPathUrls = new ArrayList <>(jarPaths.length); for (Path jarPath : jarPaths) { if (!Files.exists(jarPath) || Files.isDirectory(jarPath)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Path \"" + jarPath + "\" is not a path to a file." ); } classPathUrls.add(jarPath.toUri().toURL()); } URLClassLoader classLoader = new URLClassLoader (classPathUrls.toArray(new URL [classPathUrls.size()])); return classLoader; } public static void deleteDirectory (Path root) throws IOException { Files.walkFileTree(root, new SimpleFileVisitor <Path>() { @Override public FileVisitResult visitFile (Path file, BasicFileAttributes attrs) throws IOException { Files.delete(file); return FileVisitResult.CONTINUE; } @Override public FileVisitResult postVisitDirectory (Path dir, IOException exc) throws IOException { Files.delete(dir); return FileVisitResult.CONTINUE; } }); } public static void copy (InputStream inputStream, OutputStream outputStream) throws IOException { final byte [] buffer = new byte [4096 ]; int n; while ((n = inputStream.read(buffer)) > 0 ) { outputStream.write(buffer, 0 , n); } } }
2. ClassResourceEnumerator
定义类资源接口。
1 2 3 4 public static interface ClassResource { public InputStream getInputStream () throws IOException; public String getName () ; }
类资源具体实现:
PathClassResource:直接从路径读取类文件,用于通过 JRT 文件系统读取路径下的类文件(运行时)ClassLoaderClassResource:使用已有的 ClassLoader 读取类文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 private static class PathClassResource implements ClassResource { private final Path path; private PathClassResource (Path path) { this .path = path; } @Override public InputStream getInputStream () throws IOException { return Files.newInputStream(path); } @Override public String getName () { return path.toString(); } } private static class ClassLoaderClassResource implements ClassResource { private final ClassLoader classLoader; private final String resourceName; private ClassLoaderClassResource (ClassLoader classLoader, String resourceName) { this .classLoader = classLoader; this .resourceName = resourceName; } @Override public InputStream getInputStream () throws IOException { return classLoader.getResourceAsStream(resourceName); } @Override public String getName () { return resourceName; } }
返回运行时的所有类和指定 java 包中的类,这里的运行时类指 JDK 中的类。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 public Collection<ClassResource> getAllClasses () throws IOException { Collection<ClassResource> result = new ArrayList <>(getRuntimeClasses()); for (ClassPath.ClassInfo classInfo : ClassPath.from(classLoader).getAllClasses()) { result.add(new ClassLoaderClassResource (classLoader, classInfo.getResourceName())); } return result; } private Collection<ClassResource> getRuntimeClasses () throws IOException { URL stringClassUrl = Object.class.getResource("String.class" ); URLConnection connection = stringClassUrl.openConnection(); Collection<ClassResource> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (connection instanceof JarURLConnection) { URL runtimeUrl = ((JarURLConnection) connection).getJarFileURL(); URLClassLoader classLoader = new URLClassLoader (new URL []{runtimeUrl}); for (ClassPath.ClassInfo classInfo : ClassPath.from(classLoader).getAllClasses()) { result.add(new ClassLoaderClassResource (classLoader, classInfo.getResourceName())); } return result; } try { FileSystem fs = FileSystems.getFileSystem(URI.create("jrt:/" )); Files.walk(fs.getPath("/" )).forEach(p -> { if (p.toString().toLowerCase().endsWith(".class" )) { result.add(new PathClassResource (p)); } }); } catch (ProviderNotFoundException e) { } return result; }
3. GadgetInspector
程序入口 main,先做一些准备工作,然后分 5 步走挖掘利用链。
首先判断参数是否为空,使用 Gadget Inspector 至少要指定一个待分析的 java 包,若参数为空则打印使用帮助。
1 2 3 4 if (args.length == 0 ) { printUsage(); System.exit(1 ); }
配置日志输出、.dat 文件保留、挖掘类型。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 configureLogging(); boolean resume = false ;GIConfig config = ConfigRepository.getConfig("jserial" );
解析参数,可选参数包括:
--resume:是否保留文件,默认不保留--config xxx:指定挖掘类型,默认 Java 原生序列化 jserial
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 int argIndex = 0 ;while (argIndex < args.length) { String arg = args[argIndex]; if (!arg.startsWith("--" )) { break ; } if (arg.equals("--resume" )) { resume = true ; } else if (arg.equals("--config" )) { config = ConfigRepository.getConfig(args[++argIndex]); if (config == null ) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Invalid config name: " + args[argIndex]); } } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Unexpected argument: " + arg); } argIndex += 1 ; }
根据参数读取 war 包或 jar 包,可以指定 1 个 war 包或多个 jar 包。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 final ClassLoader classLoader;if (args.length == argIndex + 1 && args[argIndex].toLowerCase().endsWith(".war" )) { Path path = Paths.get(args[argIndex]); LOGGER.info("Using WAR classpath: " + path); classLoader = Util.getWarClassLoader(path); } else { final Path[] jarPaths = new Path [args.length - argIndex]; for (int i = 0 ; i < args.length - argIndex; i++) { Path path = Paths.get(args[argIndex + i]).toAbsolutePath(); if (!Files.exists(path)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Invalid jar path: " + path); } jarPaths[i] = path; } LOGGER.info("Using classpath: " + Arrays.toString(jarPaths)); classLoader = Util.getJarClassLoader(jarPaths); }
使用上面得到的 ClassLoader 初始化类枚举加载器。
1 final ClassResourceEnumerator classResourceEnumerator = new ClassResourceEnumerator (classLoader);
根据 resume 变量的值决定是否删除 .dat 文件,挖掘到的利用链存储在 gadget-chains.txt 中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 if (!resume) { LOGGER.info("Deleting stale data..." ); for (String datFile : Arrays.asList("classes.dat" , "methods.dat" , "inheritanceMap.dat" , "passthrough.dat" , "callgraph.dat" , "sources.dat" , "methodimpl.dat" )) { final Path path = Paths.get(datFile); if (Files.exists(path)) { Files.delete(path); } } }
挖掘过程中判断是否存在 .dat 文件,核心步骤如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 if (!Files.exists(Paths.get("classes.dat" )) || !Files.exists(Paths.get("methods.dat" )) || !Files.exists(Paths.get("inheritanceMap.dat" ))) { LOGGER.info("Running method discovery..." ); MethodDiscovery methodDiscovery = new MethodDiscovery (); methodDiscovery.discover(classResourceEnumerator); methodDiscovery.save(); } if (!Files.exists(Paths.get("passthrough.dat" ))) { LOGGER.info("Analyzing methods for passthrough dataflow..." ); PassthroughDiscovery passthroughDiscovery = new PassthroughDiscovery (); passthroughDiscovery.discover(classResourceEnumerator, config); passthroughDiscovery.save(); } if (!Files.exists(Paths.get("callgraph.dat" ))) { LOGGER.info("Analyzing methods in order to build a call graph..." ); CallGraphDiscovery callGraphDiscovery = new CallGraphDiscovery (); callGraphDiscovery.discover(classResourceEnumerator, config); callGraphDiscovery.save(); } if (!Files.exists(Paths.get("sources.dat" ))) { LOGGER.info("Discovering gadget chain source methods..." ); SourceDiscovery sourceDiscovery = config.getSourceDiscovery(); sourceDiscovery.discover(); sourceDiscovery.save(); } { LOGGER.info("Searching call graph for gadget chains..." ); GadgetChainDiscovery gadgetChainDiscovery = new GadgetChainDiscovery (config); gadgetChainDiscovery.discover(); }
核心步骤看起来有多简单实际实现就有多复杂(不是 ),下面就展开核心步骤的内容。
4. MethodDiscovery
discover 方法主要完成的是读取类文件并利用 asm 的访问者记录类信息、方法信息。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public void discover (final ClassResourceEnumerator classResourceEnumerator) throws Exception { for (ClassResourceEnumerator.ClassResource classResource : classResourceEnumerator.getAllClasses()) { try (InputStream in = classResource.getInputStream()) { ClassReader cr = new ClassReader (in); try { cr.accept(new MethodDiscoveryClassVisitor (), ClassReader.EXPAND_FRAMES); } catch (Exception e) { LOGGER.error("Exception analyzing: " + classResource.getName(), e); } } } }
MethodDiscoveryClassVisitor 类继承了 asm 中的 ClassVisitor,重写了四个访问者方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 private String name; private String superName; private String[] interfaces; boolean isInterface; private List<ClassReference.Member> members; private ClassReference.Handle classHandle; private MethodDiscoveryClassVisitor () throws SQLException { super (Opcodes.ASM6); }
visit 方法在类访问的开始时调用(即 ClassReader.accept 调用的第一个访问者方法),记录类名、父类名、接口名、是否为接口,创建动态数组用于在 visitField 中记录字段信息。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @Override public void visit (int version, int access, String name, String signature, String superName, String[] interfaces) { this .name = name; this .superName = superName; this .interfaces = interfaces; this .isInterface = (access & Opcodes.ACC_INTERFACE) != 0 ; this .members = new ArrayList <>(); this .classHandle = new ClassReference .Handle(name); super .visit(version, access, name, signature, superName, interfaces); }
visitField 方法用于记录类的字段信息,包括名称、访问标志、类型,根据访问标志 access 判断是否为静态变量,因为静态变量不可控所以不当作可能的污点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public FieldVisitor visitField (int access, String name, String desc, // 访问字段 String signature, Object value) { if ((access & Opcodes.ACC_STATIC) == 0 ) { Type type = Type.getType(desc); String typeName; if (type.getSort() == Type.OBJECT || type.getSort() == Type.ARRAY) { typeName = type.getInternalName(); } else { typeName = type.getDescriptor(); } members.add(new ClassReference .Member(name, access, new ClassReference .Handle(typeName))); } return super .visitField(access, name, desc, signature, value); }
visitMethod 方法用于记录方法信息,包括所属类名、方法名、描述符、是否为静态方法,同样根据访问标志判断是否为静态方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 @Override public MethodVisitor visitMethod (int access, String name, String desc, String signature, String[] exceptions) { boolean isStatic = (access & Opcodes.ACC_STATIC) != 0 ; discoveredMethods.add(new MethodReference ( classHandle, name, desc, isStatic)); return super .visitMethod(access, name, desc, signature, exceptions); }
visitEnd 方法在类访问结束时调用,(即 ClassReader.accept 调用的最后一个访问者方法),此时类的字段信息已经记录完毕,可以记录下完整的类信息,包括类名、父类名、接口名、是否为接口、字段信息。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 @Override public void visitEnd () { ClassReference classReference = new ClassReference ( name, superName, interfaces, isInterface, members.toArray(new ClassReference .Member[members.size()])); discoveredClasses.add(classReference); super .visitEnd(); }
save 方法存储收集到的类信息和方法信息,同时调用 InheritanceDeriver.derive 获取继承信息并保存。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public void save () throws IOException { DataLoader.saveData(Paths.get("classes.dat" ), new ClassReference .Factory(), discoveredClasses); DataLoader.saveData(Paths.get("methods.dat" ), new MethodReference .Factory(), discoveredMethods); Map<ClassReference.Handle, ClassReference> classMap = new HashMap <>(); for (ClassReference clazz : discoveredClasses) { classMap.put(clazz.getHandle(), clazz); } InheritanceDeriver.derive(classMap).save(); }
5. PassthroughDiscovery
discover 方法主要执行了三个步骤:① 搜索方法调用信息,即每个方法都调用了哪些方法;② 将调用信息进行逆拓扑排序,为了便于后续分析;③ 分析每个方法的参数,判断是否能够传递污染,即方法的返回结果是否可以被其参数影响。
例如以下两个方法中,foo 方法的返回结果可以被参数控制,而 bar 方法的返回结果无法被控制。因此如果污点(攻击者的输入数据)走到 bar 方法就不能再继续下去了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 String foo (String v) { return v; } String bar (String v) { return "test" ; }
discover 方法的具体实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 private final Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<MethodReference.Handle>> methodCalls = new HashMap <>();private Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<Integer>> passthroughDataflow;public void discover (final ClassResourceEnumerator classResourceEnumerator, final GIConfig config) throws IOException { Map<MethodReference.Handle, MethodReference> methodMap = DataLoader.loadMethods(); Map<ClassReference.Handle, ClassReference> classMap = DataLoader.loadClasses(); InheritanceMap inheritanceMap = InheritanceMap.load(); Map<String, ClassResourceEnumerator.ClassResource> classResourceByName = discoverMethodCalls(classResourceEnumerator); List<MethodReference.Handle> sortedMethods = topologicallySortMethodCalls(); passthroughDataflow = calculatePassthroughDataflow(classResourceByName, classMap, inheritanceMap, sortedMethods, config.getSerializableDecider(methodMap, inheritanceMap)); }
discoverMethodCalls 方法利用 asm 的访问者记录方法调用的方法集合信息,同时存储类名和类资源的映射关系。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 private Map<String, ClassResourceEnumerator.ClassResource> discoverMethodCalls(final ClassResourceEnumerator classResourceEnumerator) throws IOException { Map<String, ClassResourceEnumerator.ClassResource> classResourcesByName = new HashMap <>(); for (ClassResourceEnumerator.ClassResource classResource : classResourceEnumerator.getAllClasses()) { try (InputStream in = classResource.getInputStream()) { ClassReader cr = new ClassReader (in); try { MethodCallDiscoveryClassVisitor visitor = new MethodCallDiscoveryClassVisitor (Opcodes.ASM6); cr.accept(visitor, ClassReader.EXPAND_FRAMES); classResourcesByName.put(visitor.getName(), classResource); } catch (Exception e) { LOGGER.error("Error analyzing: " + classResource.getName(), e); } } } return classResourcesByName; }
MethodCallDiscoveryClassVisitor 类继承了 asm 中的 ClassVisitor,重写了三个访问者方法,并实现了一个返回类名的方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 private class MethodCallDiscoveryClassVisitor extends ClassVisitor { public MethodCallDiscoveryClassVisitor (int api) { super (api); } private String name = null ; public String getName () { return name; } ... }
visit 方法只记录了当前访问的类的名称。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @Override public void visit (int version, int access, String name, String signature, String superName, String[] interfaces) { super .visit(version, access, name, signature, superName, interfaces); if (this .name != null ) { throw new IllegalStateException ("ClassVisitor already visited a class!" ); } this .name = name; }
visitMethod 方法使用 MethodCallDiscoveryMethodVisitor 类(继承了 asm 中的 MethodVisitor)观察方法,并调用 JSRInlinerAdapter 简化代码分析。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 @Override public MethodVisitor visitMethod (int access, String name, String desc, String signature, String[] exceptions) { MethodVisitor mv = super .visitMethod(access, name, desc, signature, exceptions); MethodCallDiscoveryMethodVisitor modelGeneratorMethodVisitor = new MethodCallDiscoveryMethodVisitor ( api, mv, this .name, name, desc); return new JSRInlinerAdapter (modelGeneratorMethodVisitor, access, name, desc, signature, exceptions); }
visitEnd 方法直接调用的父类方法,在这里不重写应该可以。
1 2 3 4 @Override public void visitEnd () { super .visitEnd(); }
MethodCallDiscoveryMethodVisitor 类继承了 asm 中的 MethodVisitor,只重写了 visitMethodInsn 方法,用于访问调用方法的指令;利用 calledMethods 记录当前访问的方法调用的所有方法,然后记录到 methodCalls 变量中,这里不注意点就看混了😵。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 private class MethodCallDiscoveryMethodVisitor extends MethodVisitor { private final Set<MethodReference.Handle> calledMethods; public MethodCallDiscoveryMethodVisitor (final int api, final MethodVisitor mv, final String owner, String name, String desc) { super (api, mv); this .calledMethods = new HashSet <>(); methodCalls.put(new MethodReference .Handle(new ClassReference .Handle(owner), name, desc), calledMethods); } @Override public void visitMethodInsn (int opcode, String owner, String name, String desc, boolean itf) { calledMethods.add(new MethodReference .Handle(new ClassReference .Handle(owner), name, desc)); super .visitMethodInsn(opcode, owner, name, desc, itf); } }
topologicallySortMethodCalls 方法对方法调用的方法集合进行逆拓扑排序,用于后续判断方法参数与返回值的关系,举个例子:
方法 parentMethod 在返回前调用了 Obj.childMethod,因为 Obj.childMethod 的参数 carg 与返回值有关,同时 parentMethod 将其返回值作为自己的返回结果,所以最后可以判定 parentMethod 的参数 arg 和返回值有关。
因此要先判断子方法返回值与子方法参数的关系,再判断父方法返回值与参数的关系,这样才能判断方法参数与返回值的关系。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public String parentMethod (String arg) { String vul = Obj.childMethod(arg); return vul; } public String childMethod (String carg) { return carg.toString(); }
为了实现先判断子方法后判断父方法,这里就需要进行逆拓扑排序,逆拓扑排序使用栈实现,变量 dfsStack 和 visitedNodes 用于避免形成环,同时 visitedNodes 还可以避免重复排序,具体的排序操作由 dfsTsort 实现,所有方法调用整合为一个集合。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 private List<MethodReference.Handle> topologicallySortMethodCalls() { Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<MethodReference.Handle>> outgoingReferences = new HashMap <>(); for (Map.Entry<MethodReference.Handle, Set<MethodReference.Handle>> entry : methodCalls.entrySet()) { MethodReference.Handle method = entry.getKey(); outgoingReferences.put(method, new HashSet <>(entry.getValue())); } LOGGER.debug("Performing topological sort..." ); Set<MethodReference.Handle> dfsStack = new HashSet <>(); Set<MethodReference.Handle> visitedNodes = new HashSet <>(); List<MethodReference.Handle> sortedMethods = new ArrayList <>(outgoingReferences.size()); for (MethodReference.Handle root : outgoingReferences.keySet()) { dfsTsort(outgoingReferences, sortedMethods, visitedNodes, dfsStack, root); } LOGGER.debug(String.format("Outgoing references %d, sortedMethods %d" , outgoingReferences.size(), sortedMethods.size())); return sortedMethods; } private static void dfsTsort (Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<MethodReference.Handle>> outgoingReferences, List<MethodReference.Handle> sortedMethods, Set<MethodReference.Handle> visitedNodes, Set<MethodReference.Handle> stack, MethodReference.Handle node) { if (stack.contains(node)) { return ; } if (visitedNodes.contains(node)) { return ; } Set<MethodReference.Handle> outgoingRefs = outgoingReferences.get(node); if (outgoingRefs == null ) { return ; } stack.add(node); for (MethodReference.Handle child : outgoingRefs) { dfsTsort(outgoingReferences, sortedMethods, visitedNodes, stack, child); } stack.remove(node); visitedNodes.add(node); sortedMethods.add(node); }
最后使用 calculatePassthroughDataflow 方法判断每个方法的返回值与参数关系,首先跳过静态代码块,然后利用 asm 的访问者对逆拓扑排序得到的方法集合进行遍历和分析判断。
静态代码块在类加载时调用,只执行一次,且优先于主函数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 private static Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<Integer>> calculatePassthroughDataflow(Map<String, ClassResourceEnumerator.ClassResource> classResourceByName, Map<ClassReference.Handle, ClassReference> classMap, InheritanceMap inheritanceMap, List<MethodReference.Handle> sortedMethods, SerializableDecider serializableDecider) throws IOException { final Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<Integer>> passthroughDataflow = new HashMap <>(); for (MethodReference.Handle method : sortedMethods) { if (method.getName().equals("<clinit>" )) { continue ; } ClassResourceEnumerator.ClassResource classResource = classResourceByName.get(method.getClassReference().getName()); try (InputStream inputStream = classResource.getInputStream()) { ClassReader cr = new ClassReader (inputStream); try { PassthroughDataflowClassVisitor cv = new PassthroughDataflowClassVisitor (classMap, inheritanceMap, passthroughDataflow, serializableDecider, Opcodes.ASM6, method); cr.accept(cv, ClassReader.EXPAND_FRAMES); passthroughDataflow.put(method, cv.getReturnTaint()); } catch (Exception e) { LOGGER.error("Exception analyzing " + method.getClassReference().getName(), e); } } catch (IOException e) { LOGGER.error("Unable to analyze " + method.getClassReference().getName(), e); } } return passthroughDataflow; }
PassthroughDataflowClassVisitor 继承了 asm 中的 ClassVisitor,重写 visit 记录方法所属类的名称,重写 visitMethod 对待观察的方法用 PassthroughDataflowMethodVisitor 判断返回值与参数的关系,方法 getReturnTaint 返回能够传递污染的参数索引集合。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 private static class PassthroughDataflowClassVisitor extends ClassVisitor { Map<ClassReference.Handle, ClassReference> classMap; private final MethodReference.Handle methodToVisit; private final InheritanceMap inheritanceMap; private final Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<Integer>> passthroughDataflow; private final SerializableDecider serializableDecider; private String name; private PassthroughDataflowMethodVisitor passthroughDataflowMethodVisitor; public PassthroughDataflowClassVisitor (Map<ClassReference.Handle, ClassReference> classMap, InheritanceMap inheritanceMap, Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<Integer>> passthroughDataflow, SerializableDecider serializableDecider, int api, MethodReference.Handle methodToVisit) { super (api); this .classMap = classMap; this .inheritanceMap = inheritanceMap; this .methodToVisit = methodToVisit; this .passthroughDataflow = passthroughDataflow; this .serializableDecider = serializableDecider; } @Override public void visit (int version, int access, String name, String signature, String superName, String[] interfaces) { super .visit(version, access, name, signature, superName, interfaces); this .name = name; if (!this .name.equals(methodToVisit.getClassReference().getName())) { throw new IllegalStateException ("Expecting to visit " + methodToVisit.getClassReference().getName() + " but instead got " + this .name); } } @Override public MethodVisitor visitMethod (int access, String name, String desc, String signature, String[] exceptions) { if (!name.equals(methodToVisit.getName()) || !desc.equals(methodToVisit.getDesc())) { return null ; } if (passthroughDataflowMethodVisitor != null ) { throw new IllegalStateException ("Constructing passthroughDataflowMethodVisitor twice!" ); } MethodVisitor mv = super .visitMethod(access, name, desc, signature, exceptions); passthroughDataflowMethodVisitor = new PassthroughDataflowMethodVisitor ( classMap, inheritanceMap, this .passthroughDataflow, serializableDecider, api, mv, this .name, access, name, desc, signature, exceptions); return new JSRInlinerAdapter (passthroughDataflowMethodVisitor, access, name, desc, signature, exceptions); } public Set<Integer> getReturnTaint () { if (passthroughDataflowMethodVisitor == null ) { throw new IllegalStateException ("Never constructed the passthroughDataflowmethodVisitor!" ); } return passthroughDataflowMethodVisitor.returnTaint; } }
PassthroughDataflowMethodVisitor 继承 TaintTrackingMethodVisitor 实现,重写了其中的 4 个访问者方法:
visitCode:启动对方法代码的访问,把参数全部存到本地变量表
visitInsn:访问零操作数的指令,这里只分析返回指令
visitFieldInsn:访问字段指令,字段指令是加载或存储对象字段值的指令
visitMethodInsn:访问方法指令,方法指令是调用方法的指令
但是 TaintTrackingMethodVisitor 继承 asm 的 MethodVisitor 并重写了大量的方法,模拟 JVM 在处理方法调用中的本地变量表和操作数栈,因此实际调用的访问者方法来自 PassthroughDataflowMethodVisitor、TaintTrackingMethodVisitor、MethodVisitor 三个类。模拟是根据对字节码指令和 JVM 的了解手动进行实现(救命),先解析这里的 4 个重写方法。
数据流信息 passthroughDataflow 初始为空,集合变量 returnTaint 用于记录传递污染的参数索引。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 private static class PassthroughDataflowMethodVisitor extends TaintTrackingMethodVisitor <Integer> { private final Map<ClassReference.Handle, ClassReference> classMap; private final InheritanceMap inheritanceMap; private final Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<Integer>> passthroughDataflow; private final SerializableDecider serializableDecider; private final int access; private final String desc; private final Set<Integer> returnTaint; public PassthroughDataflowMethodVisitor (Map<ClassReference.Handle, ClassReference> classMap, InheritanceMap inheritanceMap, Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<Integer>> passthroughDataflow, SerializableDecider serializableDeciderMap, int api, MethodVisitor mv, String owner, int access, String name, String desc, String signature, String[] exceptions) { super (inheritanceMap, passthroughDataflow, api, mv, owner, access, name, desc, signature, exceptions); this .classMap = classMap; this .inheritanceMap = inheritanceMap; this .passthroughDataflow = passthroughDataflow; this .serializableDecider = serializableDeciderMap; this .access = access; this .desc = desc; returnTaint = new HashSet <>(); } ... }
visitCode 方法将被访问的方法参数记录到本地变量表中,如果是非静态方法,则添加隐式参数 this。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 @Override public void visitCode () { super .visitCode(); int localIndex = 0 ; int argIndex = 0 ; if ((this .access & Opcodes.ACC_STATIC) == 0 ) { setLocalTaint(localIndex, argIndex); localIndex += 1 ; argIndex += 1 ; } for (Type argType : Type.getArgumentTypes(desc)) { setLocalTaint(localIndex, argIndex); localIndex += argType.getSize(); argIndex += 1 ; } }
visitInsn 方法将存储在栈顶的返回值(传递污染的参数索引集合,可能为空)中的元素添加到 returnTaint。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 @Override public void visitInsn (int opcode) { switch (opcode) { case Opcodes.IRETURN: case Opcodes.FRETURN: case Opcodes.ARETURN: returnTaint.addAll(getStackTaint(0 )); break ; case Opcodes.LRETURN: case Opcodes.DRETURN: returnTaint.addAll(getStackTaint(1 )); break ; case Opcodes.RETURN: break ; default : break ; } super .visitInsn(opcode); }
visitFieldInsn 方法在读取或存储对象字段的值时调用,这里判断字段是否可序列化,如果可序列化则认为方法所属类的实例对象本身或被调用方法所属类的实例对象是受污染的,将其传递污染的参数索引集合存储到 taint 变量中。visitMethodInsn 方法中的分析。最后将栈顶(读取字段的返回值)设置为 taint,这里可能是空的 HashSet。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 @Override public void visitFieldInsn (int opcode, String owner, String name, String desc) { switch (opcode) { case Opcodes.GETSTATIC: break ; case Opcodes.PUTSTATIC: break ; case Opcodes.GETFIELD: Type type = Type.getType(desc); if (type.getSize() == 1 ) { Boolean isTransient = null ; if (!couldBeSerialized(serializableDecider, inheritanceMap, new ClassReference .Handle(type.getInternalName()))) { isTransient = Boolean.TRUE; } else { ClassReference clazz = classMap.get(new ClassReference .Handle(owner)); while (clazz != null ) { for (ClassReference.Member member : clazz.getMembers()) { if (member.getName().equals(name)) { isTransient = (member.getModifiers() & Opcodes.ACC_TRANSIENT) != 0 ; break ; } } if (isTransient != null ) { break ; } clazz = classMap.get(new ClassReference .Handle(clazz.getSuperClass())); } } Set<Integer> taint; if (!Boolean.TRUE.equals(isTransient)) { taint = getStackTaint(0 ); } else { taint = new HashSet <>(); } super .visitFieldInsn(opcode, owner, name, desc); setStackTaint(0 , taint); return ; } break ; case Opcodes.PUTFIELD: break ; default : throw new IllegalStateException ("Unsupported opcode: " + opcode); } super .visitFieldInsn(opcode, owner, name, desc);
visitMethodInsn 方法在方法调用方法时调用(绕口令呢😅)
首先记录被调用方法的参数类型(列表),根据是否为静态方法添加第一个隐式参数(被调用方法所属类的实例对象)
然后记录被调用方法的返回值类型长度(0~2),用于最后存储索引集合
模拟被调用方法的操作数栈,如果是构造方法则认为隐式参数能够传递污染,如果被调用方法在已经分析的数据流信息中则直接取出相应的参数索引集合,保存到 resultTaint 变量中
调用父类方法 TaintTrackingMethodVisitor.visitMethodInsn 执行真正的出/入栈模拟,然后将参数索引集合存储到栈顶
最后根据被调用方法的返回值类型长度将 resultTaint 也合并到栈顶
调用方法时会创建新的栈帧存储用到的相关数据,因此当调用到 visitMethodInsn 时会创建新的栈帧,其操作数栈中是被调用方法的参数(而不是当前方法)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 @Override public void visitMethodInsn (int opcode, String owner, String name, String desc, boolean itf) { Type[] argTypes = Type.getArgumentTypes(desc); if (opcode != Opcodes.INVOKESTATIC) { Type[] extendedArgTypes = new Type [argTypes.length + 1 ]; System.arraycopy(argTypes, 0 , extendedArgTypes, 1 , argTypes.length); extendedArgTypes[0 ] = Type.getObjectType(owner); argTypes = extendedArgTypes; } int retSize = Type.getReturnType(desc).getSize(); Set<Integer> resultTaint; switch (opcode) { case Opcodes.INVOKESTATIC: case Opcodes.INVOKEVIRTUAL: case Opcodes.INVOKESPECIAL: case Opcodes.INVOKEINTERFACE: final List<Set<Integer>> argTaint = new ArrayList <Set<Integer>>(argTypes.length); for (int i = 0 ; i < argTypes.length; i++) { argTaint.add(null ); } int stackIndex = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < argTypes.length; i++) { Type argType = argTypes[i]; if (argType.getSize() > 0 ) { argTaint.set(argTypes.length - 1 - i, getStackTaint(stackIndex + argType.getSize() - 1 )); } stackIndex += argType.getSize(); } if (name.equals("<init>" )) { resultTaint = argTaint.get(0 ); } else { resultTaint = new HashSet <>(); } Set<Integer> passthrough = passthroughDataflow.get(new MethodReference .Handle(new ClassReference .Handle(owner), name, desc)); if (passthrough != null ) { for (Integer passthroughDataflowArg : passthrough) { resultTaint.addAll(argTaint.get(passthroughDataflowArg)); } } break ; default : throw new IllegalStateException ("Unsupported opcode: " + opcode); } super .visitMethodInsn(opcode, owner, name, desc, itf); if (retSize > 0 ) { getStackTaint(retSize - 1 ).addAll(resultTaint); } }
save 方法和 load 方法使用工厂方法实现数据的存取。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 public void save () throws IOException { if (passthroughDataflow == null ) { throw new IllegalStateException ("Save called before discover()" ); } DataLoader.saveData(Paths.get("passthrough.dat" ), new PassThroughFactory (), passthroughDataflow.entrySet()); } public static Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<Integer>> load() throws IOException { Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<Integer>> passthroughDataflow = new HashMap <>(); for (Map.Entry<MethodReference.Handle, Set<Integer>> entry : DataLoader.loadData(Paths.get("passthrough.dat" ), new PassThroughFactory ())) { passthroughDataflow.put(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()); } return passthroughDataflow; } public static class PassThroughFactory implements DataFactory <Map.Entry<MethodReference.Handle, Set<Integer>>> { @Override public Map.Entry<MethodReference.Handle, Set<Integer>> parse(String[] fields) { ClassReference.Handle clazz = new ClassReference .Handle(fields[0 ]); MethodReference.Handle method = new MethodReference .Handle(clazz, fields[1 ], fields[2 ]); Set<Integer> passthroughArgs = new HashSet <>(); for (String arg : fields[3 ].split("," )) { if (arg.length() > 0 ) { passthroughArgs.add(Integer.parseInt(arg)); } } return new AbstractMap .SimpleEntry<>(method, passthroughArgs); } @Override public String[] serialize(Map.Entry<MethodReference.Handle, Set<Integer>> entry) { if (entry.getValue().size() == 0 ) { return null ; } final String[] fields = new String [4 ]; fields[0 ] = entry.getKey().getClassReference().getName(); fields[1 ] = entry.getKey().getName(); fields[2 ] = entry.getKey().getDesc(); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); for (Integer arg : entry.getValue()) { sb.append(Integer.toString(arg)); sb.append("," ); } fields[3 ] = sb.toString(); return fields; } }
6. TaintTrackingMethodVisitor
继承 asm 的 MethodVisitor,模拟 JVM 内存结构,即本地变量表 localVars 和操作数栈 stackVars;重写了大量方法模拟调用参数时的出/入栈操作,用于进行污点分析。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 private static class SavedVariableState <T> { List<Set<T>> localVars; List<Set<T>> stackVars; public SavedVariableState () { localVars = new ArrayList <>(); stackVars = new ArrayList <>(); } public SavedVariableState (SavedVariableState<T> copy) { this .localVars = new ArrayList <>(copy.localVars.size()); this .stackVars = new ArrayList <>(copy.stackVars.size()); for (Set<T> original : copy.localVars) { this .localVars.add(new HashSet <>(original)); } for (Set<T> original : copy.stackVars) { this .stackVars.add(new HashSet <>(original)); } } public void combine (SavedVariableState<T> copy) { for (int i = 0 ; i < copy.localVars.size(); i++) { while (i >= this .localVars.size()) { this .localVars.add(new HashSet <T>()); } this .localVars.get(i).addAll(copy.localVars.get(i)); } for (int i = 0 ; i < copy.stackVars.size(); i++) { while (i >= this .stackVars.size()) { this .stackVars.add(new HashSet <T>()); } this .stackVars.get(i).addAll(copy.stackVars.get(i)); } } }
预定义了一些数据流信息:类名,方法名,方法描述符,传递污染的参数索引。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 private static final Object[][] PASSTHROUGH_DATAFLOW = new Object [][]{ {"java/lang/Object" , "toString" , "()Ljava/lang/String;" , 0 }, {"java/io/ObjectInputStream" , "readObject" , "()Ljava/lang/Object;" , 0 }, {"java/io/ObjectInputStream" , "readFields" , "()Ljava/io/ObjectInputStream$GetField;" , 0 }, {"java/io/ObjectInputStream$GetField" , "get" , "(Ljava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;" , 0 }, {"java/lang/Object" , "getClass" , "()Ljava/lang/Class;" , 0 }, {"java/lang/Class" , "forName" , "(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/Class;" , 0 }, {"java/lang/Class" , "getMethod" , "(Ljava/lang/String;[Ljava/lang/Class;)Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;" , 0 , 1 }, {"java/lang/Class" , "getMethods" , "()[Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;" , 0 }, {"java/lang/StringBuilder" , "<init>" , "(Ljava/lang/String;)V" , 0 , 1 }, {"java/lang/StringBuilder" , "<init>" , "(Ljava/lang/CharSequence;)V" , 0 , 1 }, {"java/lang/StringBuilder" , "append" , "(Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;" , 0 , 1 }, {"java/lang/StringBuilder" , "append" , "(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;" , 0 , 1 }, {"java/lang/StringBuilder" , "append" , "(Ljava/lang/StringBuffer;)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;" , 0 , 1 }, {"java/lang/StringBuilder" , "append" , "(Ljava/lang/CharSequence;)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;" , 0 , 1 }, {"java/lang/StringBuilder" , "append" , "(Ljava/lang/CharSequence;II)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;" , 0 , 1 }, {"java/lang/StringBuilder" , "toString" , "()Ljava/lang/String;" , 0 }, {"java/io/ByteArrayInputStream" , "<init>" , "([B)V" , 1 }, {"java/io/ByteArrayInputStream" , "<init>" , "([BII)V" , 1 }, {"java/io/ObjectInputStream" , "<init>" , "(Ljava/io/InputStream;)V" , 1 }, {"java/io/File" , "<init>" , "(Ljava/lang/String;I)V" , 1 }, {"java/io/File" , "<init>" , "(Ljava/lang/String;Ljava/io/File;)V" , 1 }, {"java/io/File" , "<init>" , "(Ljava/lang/String;)V" , 1 }, {"java/io/File" , "<init>" , "(Ljava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/String;)V" , 1 }, {"java/nio/paths/Paths" , "get" , "(Ljava/lang/String;[Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/nio/file/Path;" , 0 }, {"java/net/URL" , "<init>" , "(Ljava/lang/String;)V" , 1 }, };
问题:这里实现的 visitMethodInsn 比 PassthroughDataflowMethodVisitor.visitMethodInsn 多三个判断规则,后面 CallGraphDiscovery 中的 ModelGeneratorMethodVisitor 也重写了该方法并在最后调用该父类方法,为什么不直接剥离出来?
PassthroughDataflowMethodVisitor 中存储的是参数索引,而 ModelGeneratorMethodVisitor 中存储的是 arg参数索引.字段名称
出入栈操作都在 TaintTrackingMethodVisitor 中实现
经过该方法的模拟,栈顶元素即该方法能够传递污染的参数索引集合
举个例子看一看字节码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class Main { public void main (String[] args) { String cmd = new A ().method1(args[0 ]); } public void getValue (Integer number) { String s = "100" ; Integer n = Integer.parseInt(s); n = number; String value = n.toString(); } } class A { public String method1 (String param) { return param; } }
getValue 部分的字节码,用空行分隔了上面四条语句的字节码,出现的字节码指令包括:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 public void getValue (java.lang.Integer) ; descriptor: (Ljava/lang/Integer;)V flags: ACC_PUBLIC Code: stack=1 , locals=5 , args_size=2 0 : ldc #5 2 : astore_2 3 : aload_2 4 : invokestatic #6 7 : invokestatic #7 10 : astore_3 11 : aload_1 12 : astore_3 13 : aload_3 14 : invokevirtual #8 17 : astore 4 19 : return LineNumberTable: line 6 : 0 line 7 : 3 line 9 : 11 line 10 : 13 line 11 : 19
在调用方法前,进行参数的入栈,即创建一个新的栈帧,执行完毕后继续执行下一条指令。实际上这部分的模拟不是很懂,要说汇编语言倒还会看,但是 Java 字节码也还没到那么底层,我的理解是调用函数就会创建一个栈帧,执行完毕后从系统栈弹出栈帧,那么返回结果存入上一个栈帧的操作数栈栈顶?回头等我搞明白了再补两张图…
7. CallGraphDiscovery
discover 方法利用之前得到的类信息、方法信息、继承/重写信息、数据流信息,结合 asm 访问者分析被调方法的参数是否会被调用者方法的参数所影响。
以下面 getValue 方法为例,调用了 parseInt 和 toString 两个方法,但是参数 number 只会影响到 toString。因此如果污点(攻击者的输入数据)走到 getValue 方法且参数 number 是可控的(即上一步分析能够传递污染),那么进一步只需要检查 toString 方法,而 parseInt 方法就不用再检查了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public void getValue (Integer number) { String s = "100" ; Integer n = Integer.parseInt(s); n = number; String value = n.toString(); }
discover 方法的具体实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CallGraphDiscovery.class);private final Set<GraphCall> discoveredCalls = new HashSet <>();public void discover (final ClassResourceEnumerator classResourceEnumerator, GIConfig config) throws IOException { Map<MethodReference.Handle, MethodReference> methodMap = DataLoader.loadMethods(); Map<ClassReference.Handle, ClassReference> classMap = DataLoader.loadClasses(); InheritanceMap inheritanceMap = InheritanceMap.load(); Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<Integer>> passthroughDataflow = PassthroughDiscovery.load(); SerializableDecider serializableDecider = config.getSerializableDecider(methodMap, inheritanceMap); for (ClassResourceEnumerator.ClassResource classResource : classResourceEnumerator.getAllClasses()) { try (InputStream in = classResource.getInputStream()) { ClassReader cr = new ClassReader (in); try { cr.accept(new ModelGeneratorClassVisitor (classMap, inheritanceMap, passthroughDataflow, serializableDecider, Opcodes.ASM6), ClassReader.EXPAND_FRAMES); } catch (Exception e) { LOGGER.error("Error analyzing: " + classResource.getName(), e); } } } }
ModelGeneratorClassVisitor 类继承了 asm 中的 ClassVisitor,重写了五个访问者方法,主要关注 visitMethod 中调用 ModelGeneratorMethodVisitor 对方法进行分析。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 private class ModelGeneratorClassVisitor extends ClassVisitor { private final Map<ClassReference.Handle, ClassReference> classMap; private final InheritanceMap inheritanceMap; private final Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<Integer>> passthroughDataflow; private final SerializableDecider serializableDecider; public ModelGeneratorClassVisitor (Map<ClassReference.Handle, ClassReference> classMap, InheritanceMap inheritanceMap, Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<Integer>> passthroughDataflow, SerializableDecider serializableDecider, int api) { super (api); this .classMap = classMap; this .inheritanceMap = inheritanceMap; this .passthroughDataflow = passthroughDataflow; this .serializableDecider = serializableDecider; } private String name; private String signature; private String superName; private String[] interfaces; @Override public void visit (int version, int access, String name, String signature, String superName, String[] interfaces) { super .visit(version, access, name, signature, superName, interfaces); this .name = name; this .signature = signature; this .superName = superName; this .interfaces = interfaces; } @Override public MethodVisitor visitMethod (int access, String name, String desc, String signature, String[] exceptions) { MethodVisitor mv = super .visitMethod(access, name, desc, signature, exceptions); ModelGeneratorMethodVisitor modelGeneratorMethodVisitor = new ModelGeneratorMethodVisitor (classMap, inheritanceMap, passthroughDataflow, serializableDecider, api, mv, this .name, access, name, desc, signature, exceptions); return new JSRInlinerAdapter (modelGeneratorMethodVisitor, access, name, desc, signature, exceptions); } @Override public void visitOuterClass (String owner, String name, String desc) { super .visitOuterClass(owner, name, desc); } @Override public void visitInnerClass (String name, String outerName, String innerName, int access) { super .visitInnerClass(name, outerName, innerName, access); } @Override public void visitEnd () { super .visitEnd(); } }
ModelGeneratorMethodVisitor 也继承了 TaintTrackingMethodVisitor 实现,不过只重写了其中的 3 个访问者方法
visitCode:启动对方法代码的访问,把参数全部存到本地变量表
visitFieldInsn:访问字段指令,字段指令是加载或存储对象字段值的指令
visitMethodInsn:访问方法指令,方法指令是调用方法的指令
visitCode 和 PassthroughDataflowMethodVisitor(直接存储参数索引)中的实现类似,不同的是这里将 arg 与参数索引进行拼接,存储字符串到本地变量表。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 @Override public void visitCode () { super .visitCode(); int localIndex = 0 ; int argIndex = 0 ; if ((this .access & Opcodes.ACC_STATIC) == 0 ) { setLocalTaint(localIndex, "arg" + argIndex); localIndex += 1 ; argIndex += 1 ; } for (Type argType : Type.getArgumentTypes(desc)) { setLocalTaint(localIndex, "arg" + argIndex); localIndex += argType.getSize(); argIndex += 1 ; } }
visitFieldInsn 也和 PassthroughDataflowMethodVisitor(直接存储参数索引)中的实现类似,不同的是这里将字段名称与 arg参数索引 字符串进行拼接,然后存储到栈顶。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 @Override public void visitFieldInsn (int opcode, String owner, String name, String desc) { switch (opcode) { case Opcodes.GETSTATIC: break ; case Opcodes.PUTSTATIC: break ; case Opcodes.GETFIELD: Type type = Type.getType(desc); if (type.getSize() == 1 ) { Boolean isTransient = null ; if (!couldBeSerialized(serializableDecider, inheritanceMap, new ClassReference .Handle(type.getInternalName()))) { isTransient = Boolean.TRUE; } else { ClassReference clazz = classMap.get(new ClassReference .Handle(owner)); while (clazz != null ) { for (ClassReference.Member member : clazz.getMembers()) { if (member.getName().equals(name)) { isTransient = (member.getModifiers() & Opcodes.ACC_TRANSIENT) != 0 ; break ; } } if (isTransient != null ) { break ; } clazz = classMap.get(new ClassReference .Handle(clazz.getSuperClass())); } } Set<String> newTaint = new HashSet <>(); if (!Boolean.TRUE.equals(isTransient)) { for (String s : getStackTaint(0 )) { newTaint.add(s + "." + name); } } super .visitFieldInsn(opcode, owner, name, desc); setStackTaint(0 , newTaint); return ; } break ; case Opcodes.PUTFIELD: break ; default : throw new IllegalStateException ("Unsupported opcode: " + opcode); } super .visitFieldInsn(opcode, owner, name, desc); }
visitMethodInsn 方法分析被调方法的操作数栈,栈中的元素要么为空集合,要么为能够传递污染的参数集合,模拟操作数栈的元素个数,但元素值是集合(模拟值,不是真实/实际值)。arg参数索引 的形式存储到了本地变量表,当调用其他方法时,会从本地变量表加载数据到栈中,如果用到对象字段,则以 arg参数索引.字段名称 的形式入栈,因此根据栈中元素的名称就可以得知方法的哪些参数(根据名称判断)影响了被调方法的哪些参数(已知参数个数)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 @Override public void visitMethodInsn (int opcode, String owner, String name, String desc, boolean itf) { Type[] argTypes = Type.getArgumentTypes(desc); if (opcode != Opcodes.INVOKESTATIC) { Type[] extendedArgTypes = new Type [argTypes.length + 1 ]; System.arraycopy(argTypes, 0 , extendedArgTypes, 1 , argTypes.length); extendedArgTypes[0 ] = Type.getObjectType(owner); argTypes = extendedArgTypes; } switch (opcode) { case Opcodes.INVOKESTATIC: case Opcodes.INVOKEVIRTUAL: case Opcodes.INVOKESPECIAL: case Opcodes.INVOKEINTERFACE: int stackIndex = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < argTypes.length; i++) { int argIndex = argTypes.length - 1 - i; Type type = argTypes[argIndex]; Set<String> taint = getStackTaint(stackIndex); if (taint.size() > 0 ) { for (String argSrc : taint) { if (!argSrc.substring(0 , 3 ).equals("arg" )) { throw new IllegalStateException ("Invalid taint arg: " + argSrc); } int dotIndex = argSrc.indexOf('.' ); int srcArgIndex; String srcArgPath; if (dotIndex == -1 ) { srcArgIndex = Integer.parseInt(argSrc.substring(3 )); srcArgPath = null ; } else { srcArgIndex = Integer.parseInt(argSrc.substring(3 , dotIndex)); srcArgPath = argSrc.substring(dotIndex + 1 ); } discoveredCalls.add(new GraphCall ( new MethodReference .Handle(new ClassReference .Handle(this .owner), this .name, this .desc), new MethodReference .Handle(new ClassReference .Handle(owner), name, desc), srcArgIndex, srcArgPath, argIndex)); } } stackIndex += type.getSize(); } break ; default : throw new IllegalStateException ("Unsupported opcode: " + opcode); } super .visitMethodInsn(opcode, owner, name, desc, itf); }
save 方法存储分析得到的调用关系信息。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public void save () throws IOException { DataLoader.saveData(Paths.get("callgraph.dat" ), new GraphCall .Factory(), discoveredCalls); }
8. GadgetChainDiscovery
针对不同的挖掘类型,污点源信息收集的实现不同,这里关注 Java 原生序列化的污点源,分析已经在 0x02 项目结构 - gadgetinspector/javaserial - SimpleSourceDiscovery 一节中给出。
挖掘利用链实际就是找一条从 source 点到 sink 点的路径,前面收集的信息都是为了这里的搜索做准备。
这里定义了两个类分别表示利用链和利用链上的的节点(即方法)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 private static class GadgetChain { private final List<GadgetChainLink> links; private GadgetChain (List<GadgetChainLink> links) { this .links = links; } private GadgetChain (GadgetChain gadgetChain, GadgetChainLink link) { List<GadgetChainLink> links = new ArrayList <GadgetChainLink>(gadgetChain.links); links.add(link); this .links = links; } } private static class GadgetChainLink { private final MethodReference.Handle method; private final int taintedArgIndex; private GadgetChainLink (MethodReference.Handle method, int taintedArgIndex) { this .method = method; this .taintedArgIndex = taintedArgIndex; } @Override public boolean equals (Object o) { if (this == o) return true ; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false ; GadgetChainLink that = (GadgetChainLink) o; if (taintedArgIndex != that.taintedArgIndex) return false ; return method != null ? method.equals(that.method) : that.method == null ; } @Override public int hashCode () { int result = method != null ? method.hashCode() : 0 ; result = 31 * result + taintedArgIndex; return result; } }
discover 方法首先加载方法信息、继承信息,调用 InheritanceDeriver.getAllMethodImplementations 获取方法的重写信息,分析也已经在 0x02 项目结构 一节中给出,并保存到文件中,再加载上一步得到的调用关系信息。
然后加载污点源信息,将每个 source 方法作为初始节点创建一条链,加入待分析的链集合。遍历集合中的链,取出链并从尾节点(方法)开始分析,第一次分析污点源,如果其参数索引与被调方法的参数索引相同,则创建新节点并加入链的最末端,如果被调方法不是 sink 点,则加入待分析的链集合,否则加入发现的利用链集合。之后重复上面的步骤,集合中待分析的链会越来越长,直到所有链都被弹出和分析完毕。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 public void discover () throws Exception { Map<MethodReference.Handle, MethodReference> methodMap = DataLoader.loadMethods(); InheritanceMap inheritanceMap = InheritanceMap.load(); Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<MethodReference.Handle>> methodImplMap = InheritanceDeriver.getAllMethodImplementations( inheritanceMap, methodMap); final ImplementationFinder implementationFinder = config.getImplementationFinder( methodMap, methodImplMap, inheritanceMap); try (Writer writer = Files.newBufferedWriter(Paths.get("methodimpl.dat" ))) { for (Map.Entry<MethodReference.Handle, Set<MethodReference.Handle>> entry : methodImplMap.entrySet()) { writer.write(entry.getKey().getClassReference().getName()); writer.write("\t" ); writer.write(entry.getKey().getName()); writer.write("\t" ); writer.write(entry.getKey().getDesc()); writer.write("\n" ); for (MethodReference.Handle method : entry.getValue()) { writer.write("\t" ); writer.write(method.getClassReference().getName()); writer.write("\t" ); writer.write(method.getName()); writer.write("\t" ); writer.write(method.getDesc()); writer.write("\n" ); } } } Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<GraphCall>> graphCallMap = new HashMap <>(); for (GraphCall graphCall : DataLoader.loadData(Paths.get("callgraph.dat" ), new GraphCall .Factory())) { MethodReference.Handle caller = graphCall.getCallerMethod(); if (!graphCallMap.containsKey(caller)) { Set<GraphCall> graphCalls = new HashSet <>(); graphCalls.add(graphCall); graphCallMap.put(caller, graphCalls); } else { graphCallMap.get(caller).add(graphCall); } } Set<GadgetChainLink> exploredMethods = new HashSet <>(); LinkedList<GadgetChain> methodsToExplore = new LinkedList <>(); for (Source source : DataLoader.loadData(Paths.get("sources.dat" ), new Source .Factory())) { GadgetChainLink srcLink = new GadgetChainLink (source.getSourceMethod(), source.getTaintedArgIndex()); if (exploredMethods.contains(srcLink)) { continue ; } methodsToExplore.add(new GadgetChain (Arrays.asList(srcLink))); exploredMethods.add(srcLink); } long iteration = 0 ; Set<GadgetChain> discoveredGadgets = new HashSet <>(); while (methodsToExplore.size() > 0 ) { if ((iteration % 1000 ) == 0 ) { LOGGER.info("Iteration " + iteration + ", Search space: " + methodsToExplore.size()); } iteration += 1 ; GadgetChain chain = methodsToExplore.pop(); GadgetChainLink lastLink = chain.links.get(chain.links.size() - 1 ); Set<GraphCall> methodCalls = graphCallMap.get(lastLink.method); if (methodCalls != null ) { for (GraphCall graphCall : methodCalls) { if (graphCall.getCallerArgIndex() != lastLink.taintedArgIndex) { continue ; } Set<MethodReference.Handle> allImpls = implementationFinder.getImplementations(graphCall.getTargetMethod()); for (MethodReference.Handle methodImpl : allImpls) { GadgetChainLink newLink = new GadgetChainLink (methodImpl, graphCall.getTargetArgIndex()); if (exploredMethods.contains(newLink)) { continue ; } GadgetChain newChain = new GadgetChain (chain, newLink); if (isSink(methodImpl, graphCall.getTargetArgIndex(), inheritanceMap)) { discoveredGadgets.add(newChain); } else { methodsToExplore.add(newChain); exploredMethods.add(newLink); } } } } } try (OutputStream outputStream = Files.newOutputStream(Paths.get("gadget-chains.txt" )); Writer writer = new OutputStreamWriter (outputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8)) { for (GadgetChain chain : discoveredGadgets) { printGadgetChain(writer, chain); } } LOGGER.info("Found {} gadget chains." , discoveredGadgets.size()); }
isSink 方法判断方法(和参数)是否触发预定义的 JDK 中的 sink 点,比如 Runtime.exec 方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 private boolean isSink (MethodReference.Handle method, int argIndex, InheritanceMap inheritanceMap) { if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/io/FileInputStream" ) && method.getName().equals("<init>" )) { return true ; } if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/io/FileOutputStream" ) && method.getName().equals("<init>" )) { return true ; } if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/nio/file/Files" ) && (method.getName().equals("newInputStream" ) || method.getName().equals("newOutputStream" ) || method.getName().equals("newBufferedReader" ) || method.getName().equals("newBufferedWriter" ))) { return true ; } if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/lang/Runtime" ) && method.getName().equals("exec" )) { return true ; } if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/lang/reflect/Method" ) && method.getName().equals("invoke" ) && argIndex == 0 ) { return true ; } if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/net/URLClassLoader" ) && method.getName().equals("newInstance" )) { return true ; } if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/lang/System" ) && method.getName().equals("exit" )) { return true ; } if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/lang/Shutdown" ) && method.getName().equals("exit" )) { return true ; } if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/lang/Runtime" ) && method.getName().equals("exit" )) { return true ; } if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/nio/file/Files" ) && method.getName().equals("newOutputStream" )) { return true ; } if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/lang/ProcessBuilder" ) && method.getName().equals("<init>" ) && argIndex > 0 ) { return true ; } if (inheritanceMap.isSubclassOf(method.getClassReference(), new ClassReference .Handle("java/lang/ClassLoader" )) && method.getName().equals("<init>" )) { return true ; } if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/net/URL" ) && method.getName().equals("openStream" )) { return true ; } if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("org/codehaus/groovy/runtime/InvokerHelper" ) && method.getName().equals("invokeMethod" ) && argIndex == 1 ) { return true ; } if (inheritanceMap.isSubclassOf(method.getClassReference(), new ClassReference .Handle("groovy/lang/MetaClass" )) && Arrays.asList("invokeMethod" , "invokeConstructor" , "invokeStaticMethod" ).contains(method.getName())) { return true ; } if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("org/python/core/PyCode" ) && method.getName().equals("call" )) { return true ; } return false ; }
printGadgetChain 方法用于输出利用链信息。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 private static void printGadgetChain (Writer writer, GadgetChain chain) throws IOException { writer.write(String.format("%s.%s%s (%d)%n" , chain.links.get(0 ).method.getClassReference().getName(), chain.links.get(0 ).method.getName(), chain.links.get(0 ).method.getDesc(), chain.links.get(0 ).taintedArgIndex)); for (int i = 1 ; i < chain.links.size(); i++) { writer.write(String.format(" %s.%s%s (%d)%n" , chain.links.get(i).method.getClassReference().getName(), chain.links.get(i).method.getName(), chain.links.get(i).method.getDesc(), chain.links.get(i).taintedArgIndex)); } writer.write("\n" ); }
0x04 结语
测试时发现 Gadget Inspector 无法分析用 Java16 生成的 jar 包,听说 Java8 的兼容性比较好,尝试使用 Java8 打包,可以正常执行分析,之后再补充例子。
这个工具很明显无法搜索所有的利用链,为了避免路径爆炸对每个方法只访问一次,可以用最大深度限制修改;另外也有文章分析表示生成的调用关系不够全,我没有验证过;扩充的话可以从添加 source/sink 点(规则)开始,也有人扩充了对 SQL 注入(Web)的检测之类的。
当然还是先熟悉工具的运行原理,用简单的程序测试之后,再拿实际例子(比如 ysoserial)测,难顶🤯。
参阅